Syndecan-3 is selectively pro-inflammatory in the joint and contributes to antigen-induced arthritis in mice, Arthritis Research & Therapy
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 24 fevereiro 2025
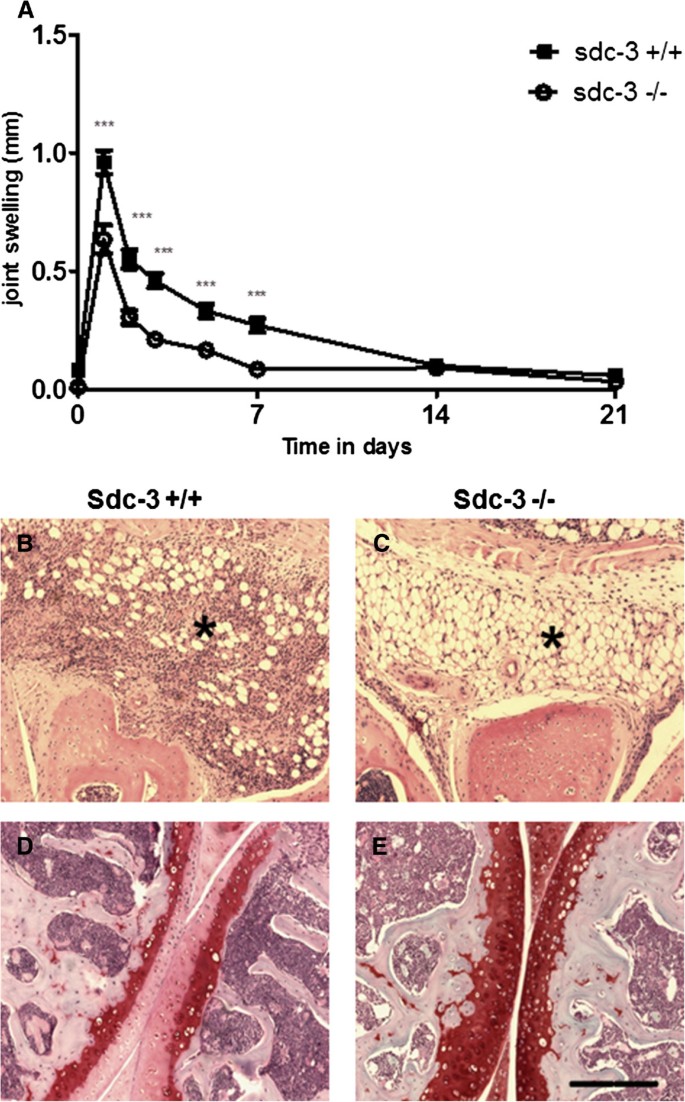
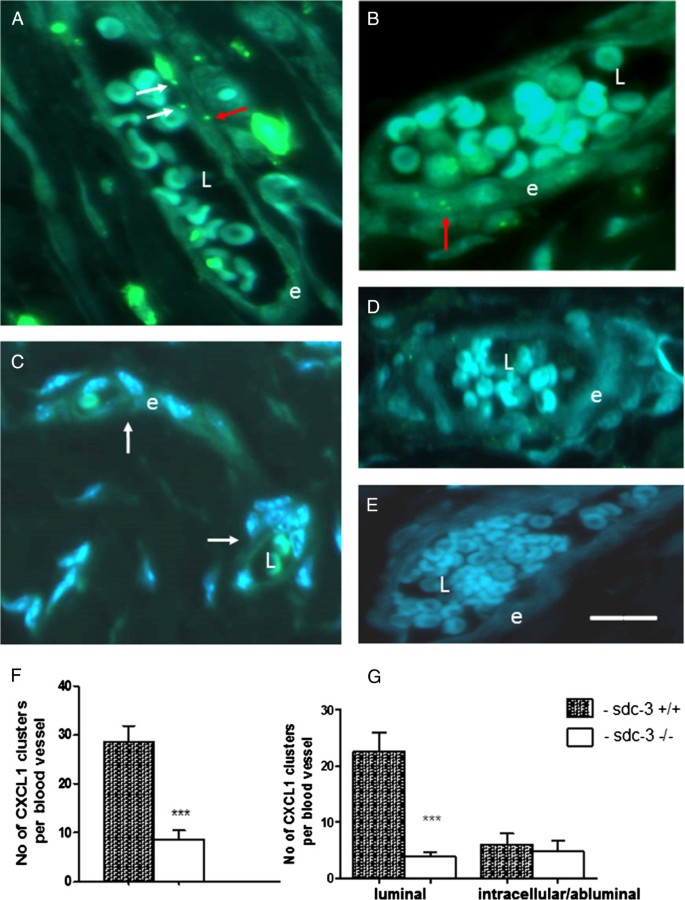
Introduction Syndecans are heparan sulphate proteoglycans expressed by endothelial cells. Syndecan-3 is expressed by synovial endothelial cells of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients where it binds chemokines, suggesting a role in leukocyte trafficking. The objective of the current study was to examine the function of syndecan-3 in joint inflammation by genetic deletion in mice and compare with other tissues. Methods Chemokine C-X-C ligand 1 (CXCL1) was injected in the joints of syndecan-3−/−and wild-type mice and antigen-induced arthritis performed. For comparison chemokine was administered in the skin and cremaster muscle. Intravital microscopy was performed in the cremaster muscle. Results Administration of CXCL1 in knee joints of syndecan-3−/−mice resulted in reduced neutrophil accumulation compared to wild type. This was associated with diminished presence of CXCL1 at the luminal surface of synovial endothelial cells where this chemokine clustered and bound to heparan sulphate. Furthermore, in the arthritis model syndecan-3 deletion led to reduced joint swelling, leukocyte accumulation, cartilage degradation and overall disease severity. Conversely, CXCL1 administration in the skin of syndecan-3 null mice provoked increased neutrophil recruitment and was associated with elevated luminal expression of E-selectin by dermal endothelial cells. Similarly in the cremaster, intravital microscopy showed increased numbers of leukocytes adhering and rolling in venules in syndecan-3−/−mice in response to CXCL1 or tumour necrosis factor alpha. Conclusions This study shows a novel role for syndecan-3 in inflammation. In the joint it is selectively pro-inflammatory, functioning in endothelial chemokine presentation and leukocyte recruitment and cartilage damage in an RA model. Conversely, in skin and cremaster it is anti-inflammatory.
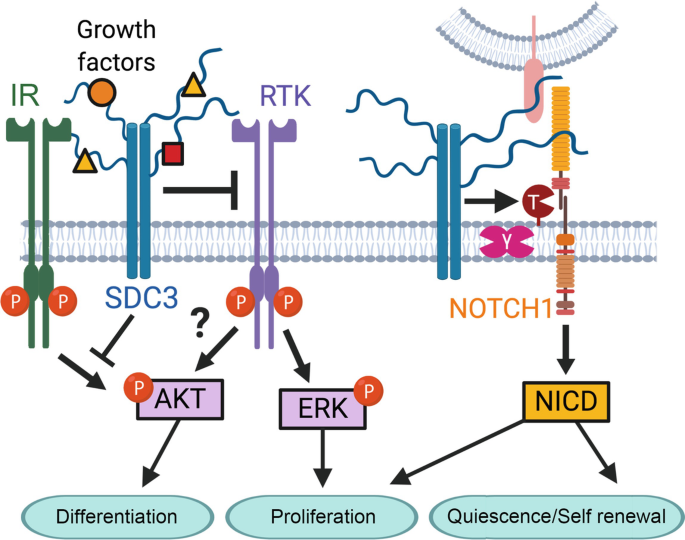
Syndecan-3: A Signaling Conductor in the Musculoskeletal System

Emerging proteoglycans and proteoglycan-targeted therapies in rheumatoid arthritis

Syndecans Circulation Research

Exploiting CD22 To Selectively Tolerize Autoantibody Producing B-Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis

Antigen-induced arthritis in sdc-3−/−and wild-type mice. Arthritis was

Effects of Inflammation on Multiscale Biomechanical Properties of Cartilaginous Cells and Tissues
IJMS, Free Full-Text
Syndecan-3 is selectively pro-inflammatory in the joint and contributes to antigen-induced arthritis in mice, Arthritis Research & Therapy

Synovial tissues concentrate secreted APRIL – topic of research paper in Clinical medicine. Download scholarly article PDF and read for free on CyberLeninka open science hub.

Replenishing decoy extracellular vesicles inhibits phenotype remodeling of tissue-resident cells in inflammation-driven arthritis - ScienceDirect

Cartilage extracellular matrix-derived matrikines in osteoarthritis
Recomendado para você
-
 The Faux Pas Films Complete Collection DVD24 fevereiro 2025
The Faux Pas Films Complete Collection DVD24 fevereiro 2025 -
 Most Disturbed Person on Planet Earth (2013) - IMDb24 fevereiro 2025
Most Disturbed Person on Planet Earth (2013) - IMDb24 fevereiro 2025 -
![NSFW] Death Films Iceberg : r/IcebergCharts](https://i.redd.it/fqj64ylb8ty61.jpg) NSFW] Death Films Iceberg : r/IcebergCharts24 fevereiro 2025
NSFW] Death Films Iceberg : r/IcebergCharts24 fevereiro 2025 -
MDPOPE Radio - playlist by Spotify24 fevereiro 2025
-
 100 ONE HIT WONDERS - 100 One Hit Wonders - Music24 fevereiro 2025
100 ONE HIT WONDERS - 100 One Hit Wonders - Music24 fevereiro 2025 -
 mdpope1|TikTok Search24 fevereiro 2025
mdpope1|TikTok Search24 fevereiro 2025 -
 L'Auberge Espagnole - 2 DVD - Romain Duris - Cecile Of France - Judith Godrèche24 fevereiro 2025
L'Auberge Espagnole - 2 DVD - Romain Duris - Cecile Of France - Judith Godrèche24 fevereiro 2025 -
MD POPE III|TikTok Search24 fevereiro 2025
-
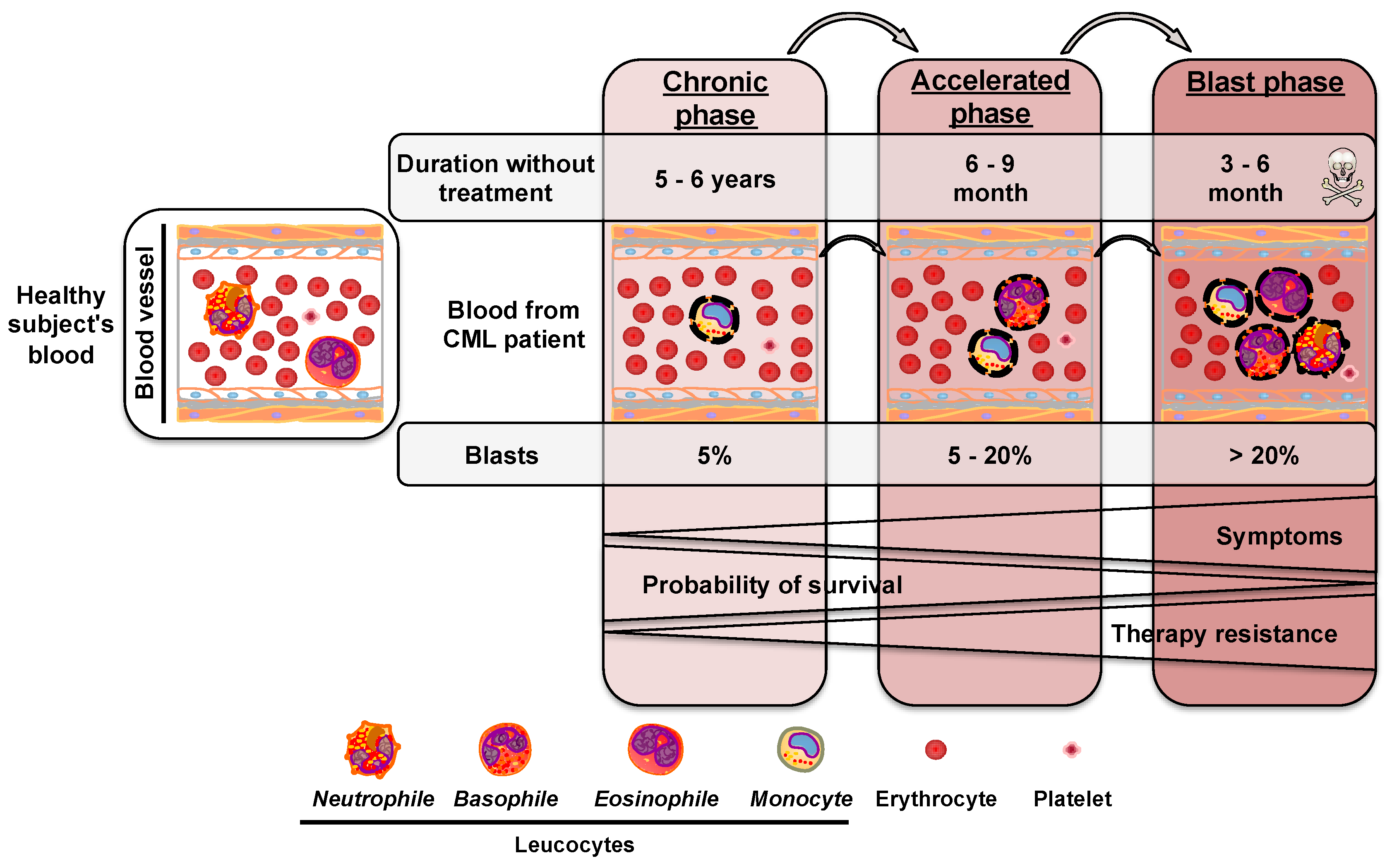 Cancers, Free Full-Text24 fevereiro 2025
Cancers, Free Full-Text24 fevereiro 2025 -
 Exhumation – Song by MDPOPE – Apple Music24 fevereiro 2025
Exhumation – Song by MDPOPE – Apple Music24 fevereiro 2025
você pode gostar
-
Fluminense Campeão Mundial - Copa Rio 1952 - postal_02_sporting_24 fevereiro 2025
-
 The Ultimate Minecraft Quiz24 fevereiro 2025
The Ultimate Minecraft Quiz24 fevereiro 2025 -
Square Enix terá aplicativo próprio na PlayStation Store24 fevereiro 2025
-
 FNAF DOOM 1 Parte 124 fevereiro 2025
FNAF DOOM 1 Parte 124 fevereiro 2025 -
 Halo TV Show Introduces The Hunters' True Look That The Games Ignore24 fevereiro 2025
Halo TV Show Introduces The Hunters' True Look That The Games Ignore24 fevereiro 2025 -
 Avançado ex-FC Porto e defesa ex-Sporting afastados do plantel do Besiktas24 fevereiro 2025
Avançado ex-FC Porto e defesa ex-Sporting afastados do plantel do Besiktas24 fevereiro 2025 -
 Stream Barbie Dreamhouse Adventures Jogo Apk from CalatFiryo24 fevereiro 2025
Stream Barbie Dreamhouse Adventures Jogo Apk from CalatFiryo24 fevereiro 2025 -
 Exército brasileiro pretende criar jogo de guerra patriótico - TecMundo24 fevereiro 2025
Exército brasileiro pretende criar jogo de guerra patriótico - TecMundo24 fevereiro 2025 -
 Afro Samurai 4 Afro samurai, Samurai anime, Samurai art24 fevereiro 2025
Afro Samurai 4 Afro samurai, Samurai anime, Samurai art24 fevereiro 2025 -
 Alistamento militar 2020 pode ser feito pela internet24 fevereiro 2025
Alistamento militar 2020 pode ser feito pela internet24 fevereiro 2025


