Differential cellular stiffness contributes to tissue elongation on an expanding surface
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 03 fevereiro 2025


Mechanical Regulation of Transcription: Recent Advances: Trends in Cell Biology

Increase of Cortical Tension and Stiffness during Normal Gastrulation

Differential cellular stiffness contributes to tissue elongation on an expanding surface

Cellular Heterogeneity in Pressure and Growth Emerges from Tissue Topology and Geometry - ScienceDirect

An overview of substrate stiffness guided cellular response and its applications in tissue regeneration - ScienceDirect
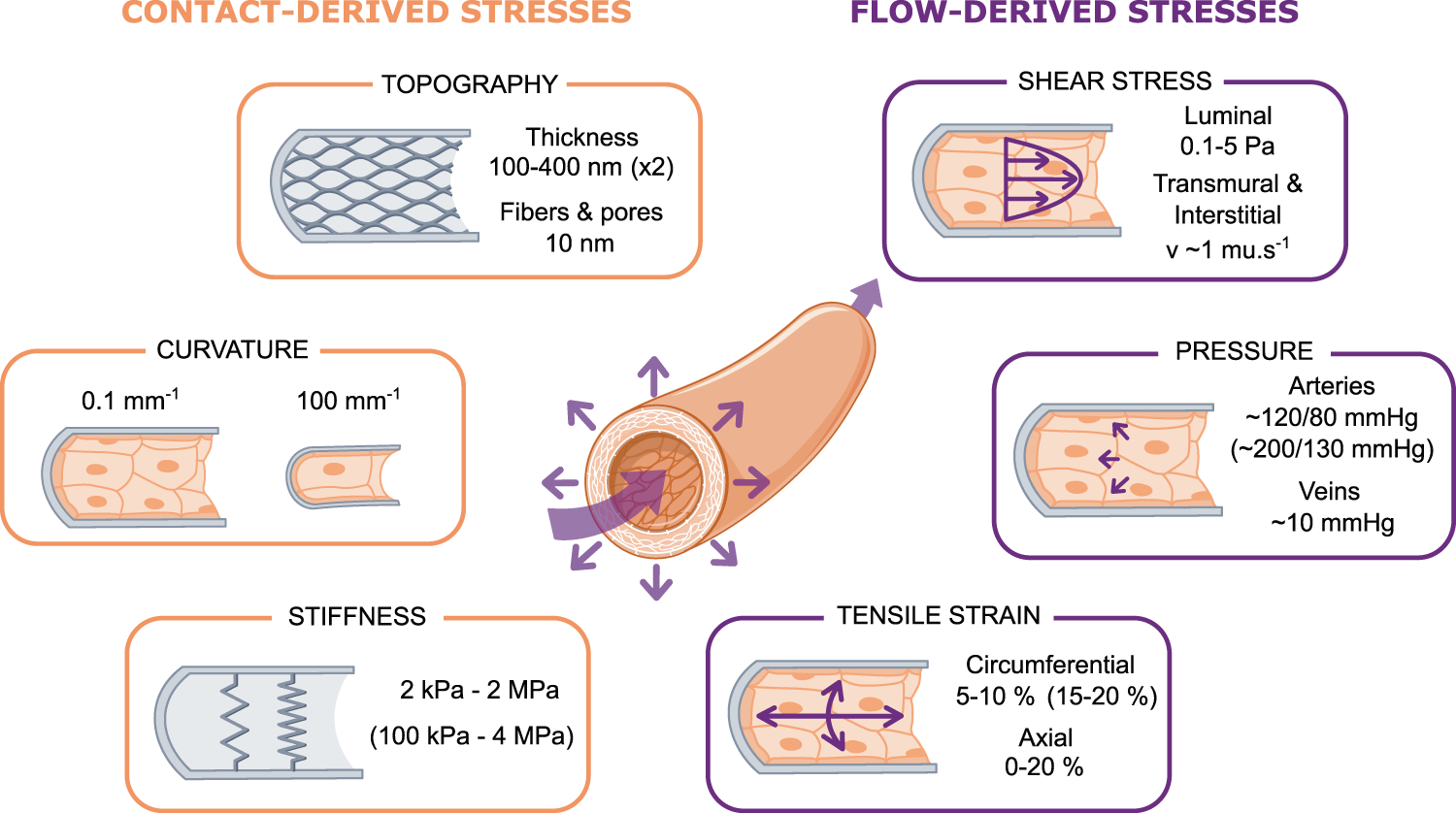
Integration of substrate- and flow-derived stresses in endothelial cell mechanobiology

Physicochemical Tools for Visualizing and Quantifying Cell-Generated Forces
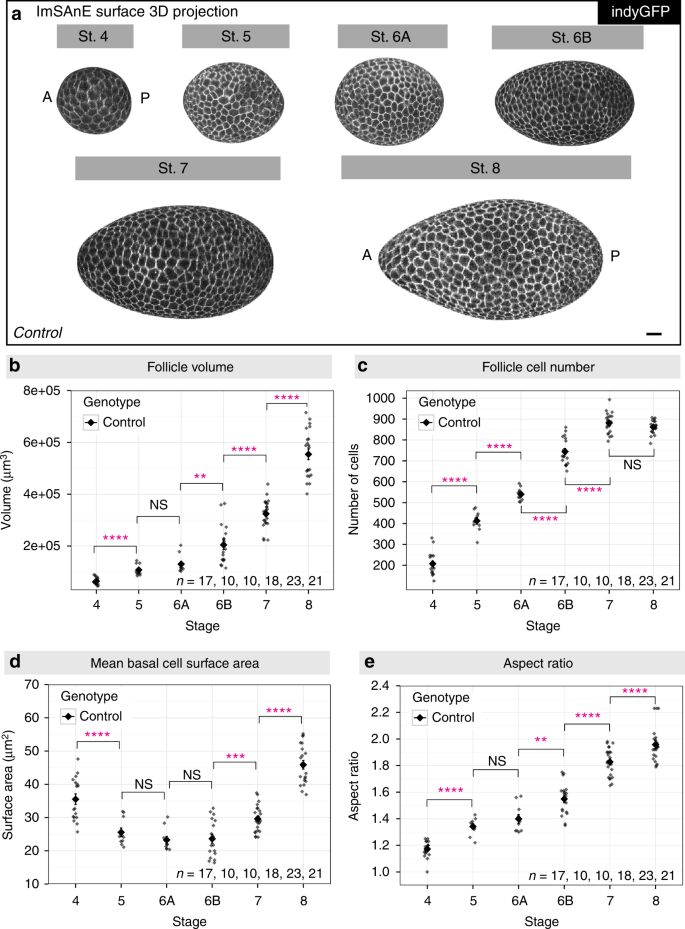
Extracellular matrix stiffness cues junctional remodeling for 3D tissue elongation
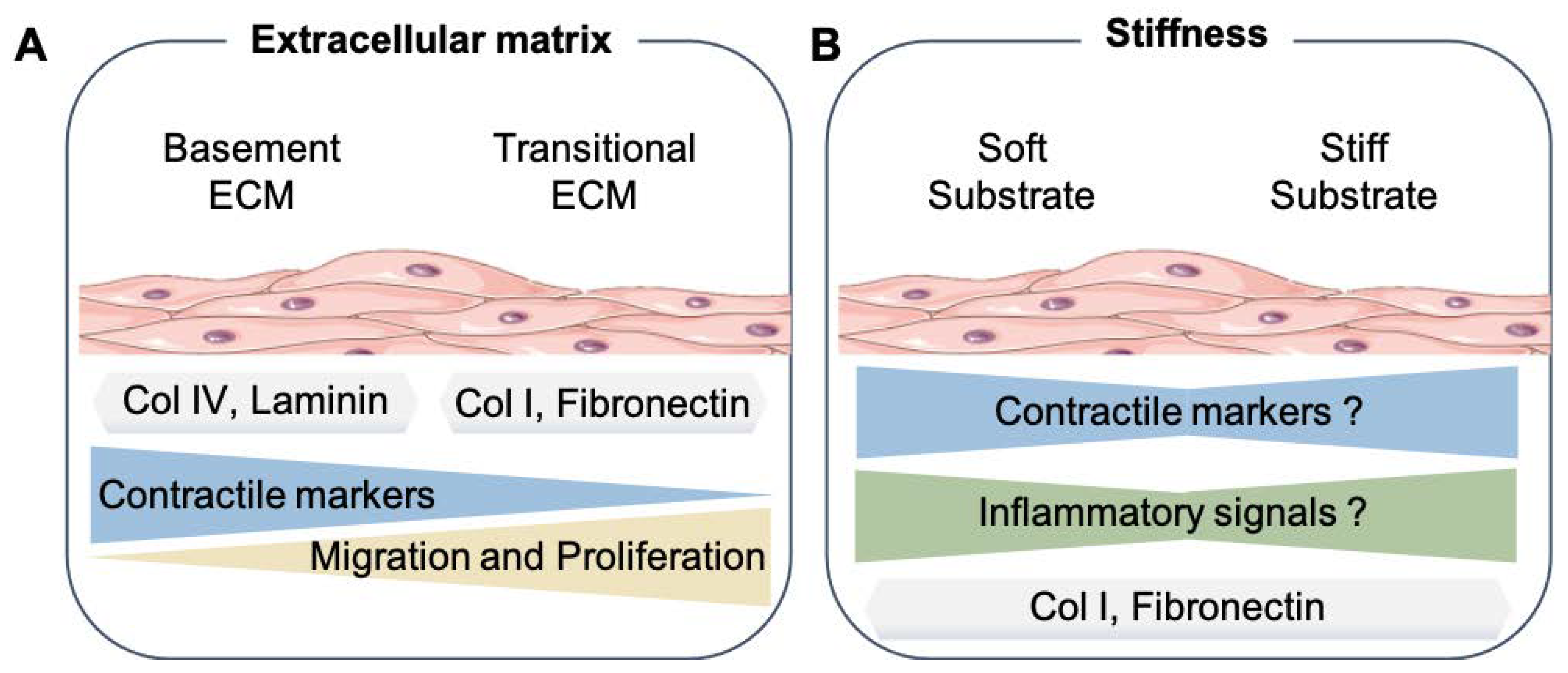
Cells, Free Full-Text
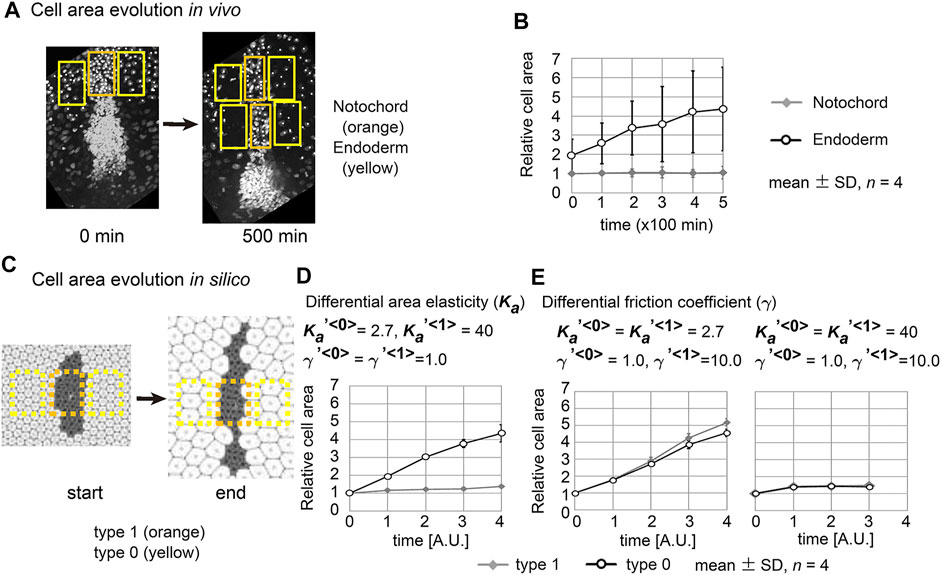
Frontiers Differential Cellular Stiffness Contributes to Tissue Elongation on an Expanding Surface
Recomendado para você
-
 U played (jessie murph cover;djons prod.remix) (TIK TOK)03 fevereiro 2025
U played (jessie murph cover;djons prod.remix) (TIK TOK)03 fevereiro 2025 -
 Stream U Played (feat. Lil Baby) by MoneyBagg Yo03 fevereiro 2025
Stream U Played (feat. Lil Baby) by MoneyBagg Yo03 fevereiro 2025 -
 iBloom chocolate mint banana squishy03 fevereiro 2025
iBloom chocolate mint banana squishy03 fevereiro 2025 -
 Moneybagg Yo - U Played (feat. Lil Baby) (Lyrics)03 fevereiro 2025
Moneybagg Yo - U Played (feat. Lil Baby) (Lyrics)03 fevereiro 2025 -
 Cute Chiko chicken to light up your keyboard >o< Anyone like these little pastel keycaps? 🙋♀️ : r/MechanicalKeyboards03 fevereiro 2025
Cute Chiko chicken to light up your keyboard >o< Anyone like these little pastel keycaps? 🙋♀️ : r/MechanicalKeyboards03 fevereiro 2025 -
 NACODEX Mini 60% Mechanical Gaming Keyboard - PBT Pudding Keycap Bluetooth 5.0 Rainbow Keyboard - 1000mAh Ultra-Compact Keyboard for Win/Mac/PC Gamer (Blue Switch Black) : Video Games03 fevereiro 2025
NACODEX Mini 60% Mechanical Gaming Keyboard - PBT Pudding Keycap Bluetooth 5.0 Rainbow Keyboard - 1000mAh Ultra-Compact Keyboard for Win/Mac/PC Gamer (Blue Switch Black) : Video Games03 fevereiro 2025 -
 3D Cute Corgi Soft Squishy Butt Phone Case For Xiaomi Redmi 12C A1 Poco F4 F3 X4 X3 GT Mi 12 11I 10 9 10T Plush Soft Cover Coque03 fevereiro 2025
3D Cute Corgi Soft Squishy Butt Phone Case For Xiaomi Redmi 12C A1 Poco F4 F3 X4 X3 GT Mi 12 11I 10 9 10T Plush Soft Cover Coque03 fevereiro 2025 -
 Viewfinder vs capturing a photo in Whatsapp on Xiaomi EU 12.5.19 - POCO F3. Any one facing the same issue? It always adds more space to the right side : r/PocoPhones03 fevereiro 2025
Viewfinder vs capturing a photo in Whatsapp on Xiaomi EU 12.5.19 - POCO F3. Any one facing the same issue? It always adds more space to the right side : r/PocoPhones03 fevereiro 2025 -
 Razer Nostromo PC Gaming Keypad : Electronics03 fevereiro 2025
Razer Nostromo PC Gaming Keypad : Electronics03 fevereiro 2025 -
 Folding Keyboard, iClever Bluetooth Travel Keyboard, Sync Up to 3 Devices, Metal Build, USB-C Recharge, Portable Foldable Keyboard with Stand Holder for iPad, iPhone, Smartphone, Laptop and Tablet : Electronics03 fevereiro 2025
Folding Keyboard, iClever Bluetooth Travel Keyboard, Sync Up to 3 Devices, Metal Build, USB-C Recharge, Portable Foldable Keyboard with Stand Holder for iPad, iPhone, Smartphone, Laptop and Tablet : Electronics03 fevereiro 2025
você pode gostar
-
 There is this video game accurate freddy plush I found looking for new fnaf movie products : r/fivenightsatfreddys03 fevereiro 2025
There is this video game accurate freddy plush I found looking for new fnaf movie products : r/fivenightsatfreddys03 fevereiro 2025 -
 DEMON SLAYER EYE QUIZ 👺👀 Kimetsu No Yaiba Quiz 👹⚔️ Mr. Ding03 fevereiro 2025
DEMON SLAYER EYE QUIZ 👺👀 Kimetsu No Yaiba Quiz 👹⚔️ Mr. Ding03 fevereiro 2025 -
 D-BOX News Assassin's Creed® Valhalla soon compatible in D-BOX03 fevereiro 2025
D-BOX News Assassin's Creed® Valhalla soon compatible in D-BOX03 fevereiro 2025 -
 Counter Strike 2 Release Date And First View: A New Era03 fevereiro 2025
Counter Strike 2 Release Date And First View: A New Era03 fevereiro 2025 -
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/TermDefinitions_PercapitaGDP-09e9332fe3d04e68b34e676554168077.jpg) GDP Per Capita: Definition, Uses, and Highest Per Country03 fevereiro 2025
GDP Per Capita: Definition, Uses, and Highest Per Country03 fevereiro 2025 -
 Here Is The FIRST EVER Gaming Video On !03 fevereiro 2025
Here Is The FIRST EVER Gaming Video On !03 fevereiro 2025 -
Bolo Maquiagem! - Meu Pote Gourmet03 fevereiro 2025
-
Crunchyroll Games - Miss Yukime 😳🤍 (via The Eminence in03 fevereiro 2025
-
 The Chosen One, Book by David Owen, Official Publisher Page03 fevereiro 2025
The Chosen One, Book by David Owen, Official Publisher Page03 fevereiro 2025 -
 Dual Guns List - Mabinogi World Wiki03 fevereiro 2025
Dual Guns List - Mabinogi World Wiki03 fevereiro 2025

