Comparison of AaL active site with AiiA, AiiB, and AidC. (A)
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 26 junho 2024


Structural and Biochemical Characterization of AidC, a Quorum-Quenching Lactonase with Atypical Selectivity. - Abstract - Europe PMC
Marine Drugs, Free Full-Text

WO2020185861A1 - Proteins and methods for disrupting bacterial communication - Google Patents

Comparison of AaL active site with AiiA, AiiB, and AidC. (A)
Cloning and characterization of Aiia, an acylhomoserine lactonase from Bacillus cereus RC1 to control soft rot causing pathogen Lelliottia amnigena RCE

SsoPox W263 saturation site screening and characterization. A. Relative

Engineering acyl-homoserine lactone-interfering enzymes toward bacterial control - ScienceDirect

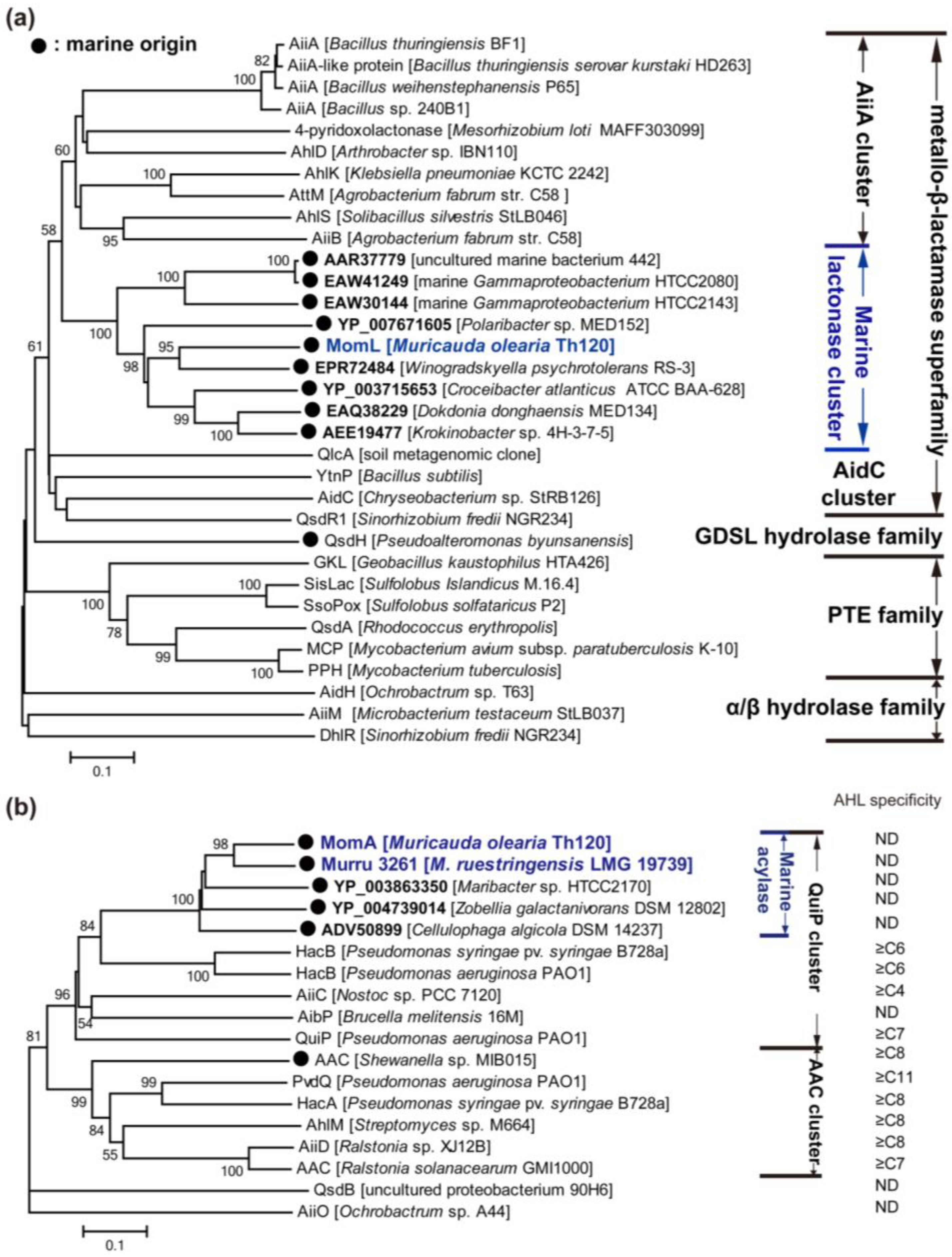
MomL, a Novel Marine-Derived N-Acyl Homoserine Lactonase from Muricauda olearia

Mechanism of the Quorum-Quenching Lactonase (AiiA) from Bacillus thuringiensis. 2. Substrate Modeling and Active Site Mutations

Identification of N‐acyl homoserine lactone‐degrading bacteria isolated from rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) - Torabi Delshad - 2018 - Journal of Applied Microbiology - Wiley Online Library

MomL, a Novel Marine-Derived N-Acyl Homoserine Lactonase from Muricauda olearia
Recomendado para você
-
 Viktor Rydberg — Teutonic Mythology — Contents26 junho 2024
Viktor Rydberg — Teutonic Mythology — Contents26 junho 2024 -
Asgard (@asgard49)'s videos with Originalton - Asgard26 junho 2024
-
 Reflex 2021 Clothing Catalogue by Reflex Marketing - Issuu26 junho 2024
Reflex 2021 Clothing Catalogue by Reflex Marketing - Issuu26 junho 2024 -
 Scotts (Clyde)26 junho 2024
Scotts (Clyde)26 junho 2024 -
 124等、大主教、希望綠洲】持續升級當中圖片在內已經很便宜了,資源蠻26 junho 2024
124等、大主教、希望綠洲】持續升級當中圖片在內已經很便宜了,資源蠻26 junho 2024 -
 BusinessMirror November 08, 2019 by BusinessMirror - Issuu26 junho 2024
BusinessMirror November 08, 2019 by BusinessMirror - Issuu26 junho 2024 -
The Truth About Solar Panel Performance and Temperature26 junho 2024
-
 Life 👨🍼💔quotes #life #motivation #lifequotes #quotes #alone26 junho 2024
Life 👨🍼💔quotes #life #motivation #lifequotes #quotes #alone26 junho 2024 -
Drut spawalniczy MIG MIGOMAT SG2 SZPULA 1kg 0,8 mm (Drut26 junho 2024
-
song finder online url26 junho 2024
você pode gostar
-
 Read Oshi No Ko Manga Online26 junho 2024
Read Oshi No Ko Manga Online26 junho 2024 -
 Pokémon Giratina Plush • Magic Plush26 junho 2024
Pokémon Giratina Plush • Magic Plush26 junho 2024 -
 Valve's Gabe Newell Throws Down Gauntlet, Makes Steam Password Public26 junho 2024
Valve's Gabe Newell Throws Down Gauntlet, Makes Steam Password Public26 junho 2024 -
 The Master of Ragnarok & Blesser of Einherjar (Hyakuren no Haou to26 junho 2024
The Master of Ragnarok & Blesser of Einherjar (Hyakuren no Haou to26 junho 2024 -
 This is the Rolls-Royce SUV. Kind of26 junho 2024
This is the Rolls-Royce SUV. Kind of26 junho 2024 -
Divertindo com a Matemática: Problema de Lógica - Amigas da Escola26 junho 2024
-
 Scream 1001, Roblox Creepypasta Wiki26 junho 2024
Scream 1001, Roblox Creepypasta Wiki26 junho 2024 -
 LEGO® Marvel™ Super Heroes26 junho 2024
LEGO® Marvel™ Super Heroes26 junho 2024 -
 God of Martial Arts - Capítulo 19.3 por Saikai Scan26 junho 2024
God of Martial Arts - Capítulo 19.3 por Saikai Scan26 junho 2024 -
 FREE 4 ESTRELAS! QUAL DELES É O MELHOR PARA SUA CONTA? - GENSHIN IMPACT26 junho 2024
FREE 4 ESTRELAS! QUAL DELES É O MELHOR PARA SUA CONTA? - GENSHIN IMPACT26 junho 2024

