Site-specific phosphorylations of the Arf activator GBF1 differentially regulate GBF1 function in Golgi homeostasis and secretion versus cytokinesis
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 28 dezembro 2024
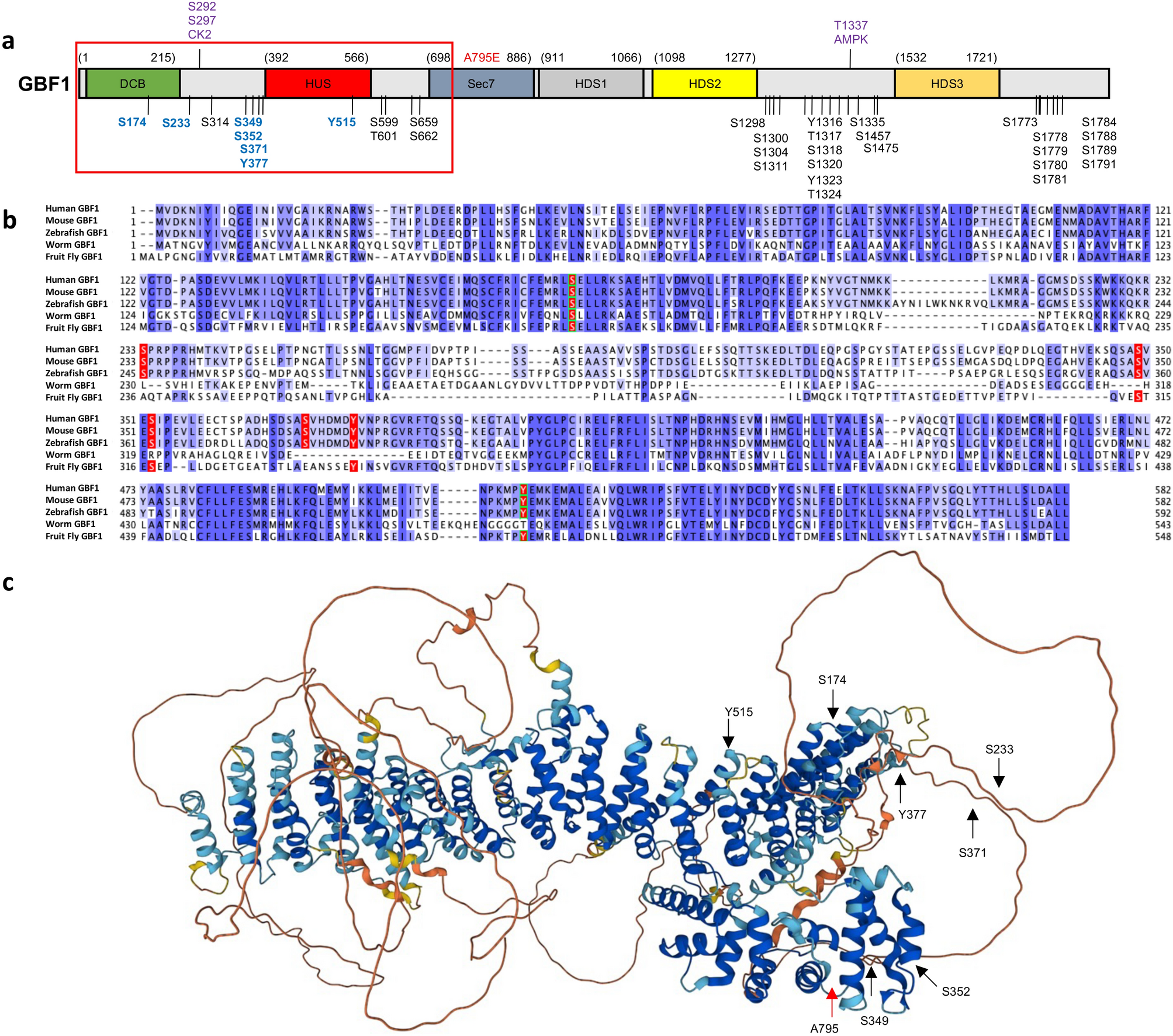

ADP-Ribosylation Factor/COPI-dependent Events at the Endoplasmic Reticulum- Golgi Interface Are Regulated by the Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor GBF1

Oligomerization of the Sec7 domain Arf guanine nucleotide exchange factor GBF1 is dispensable for Golgi localization and function but regulates degradation
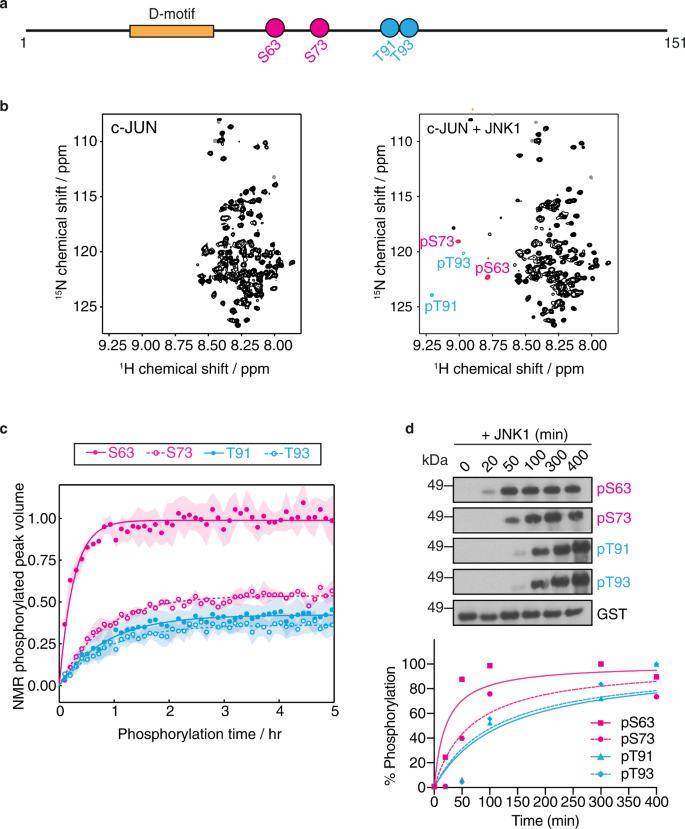
An intrinsic temporal order of c-JUN N-terminal phosphorylation regulates its activity by orchestrating co-factor recruitment

The Golgi apparatus: Lessons from Drosophila - ScienceDirect

The inhibition of cytoplasmic dynein motor activity reduces GBF1
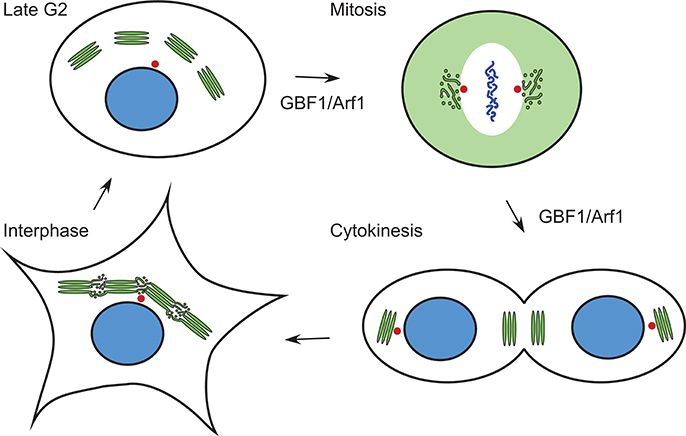
Frontiers Activators and Effectors of the Small G Protein Arf1 in Regulation of Golgi Dynamics During the Cell Division Cycle

A- Immmunoprecipitation (IP) of endogenous proteins. In the left panel

GBF1 sequence determines BFA resistance of cells and virus. A.

Model for Arf activation at the Golgi. The Arf GEF GBF1 (red) and
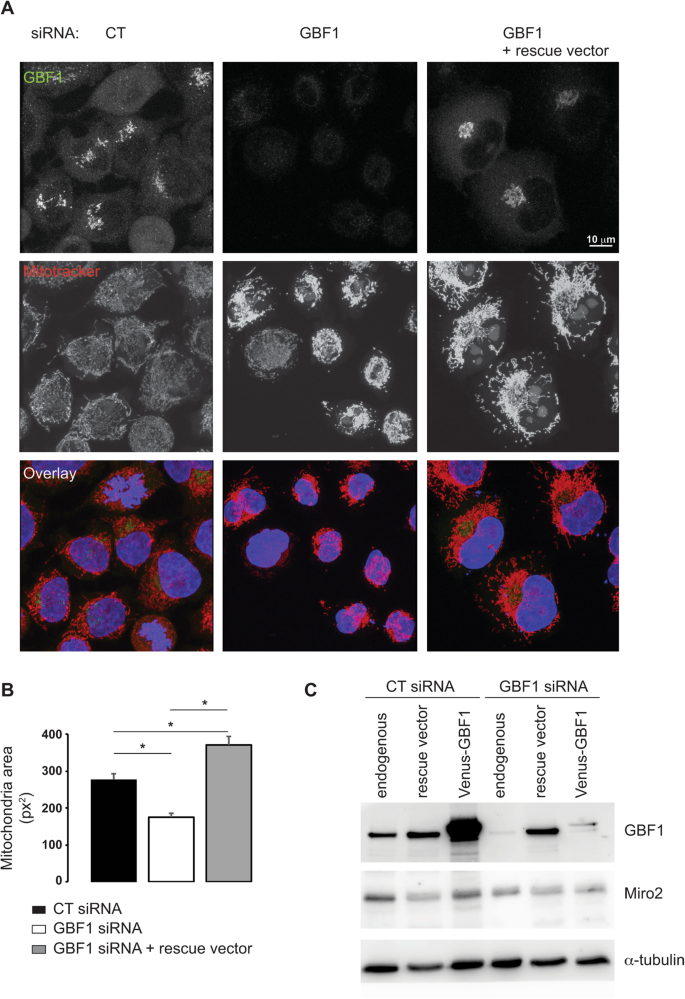
GBF1 and Arf1 interact with Miro and regulate mitochondrial positioning within cells

Dynamics of GBF1, a Brefeldin A-Sensitive Arf1 Exchange Factor at the Golgi
Simulation fits of FRAP data. HeLa cells co-expressing GFP-GBF1 and
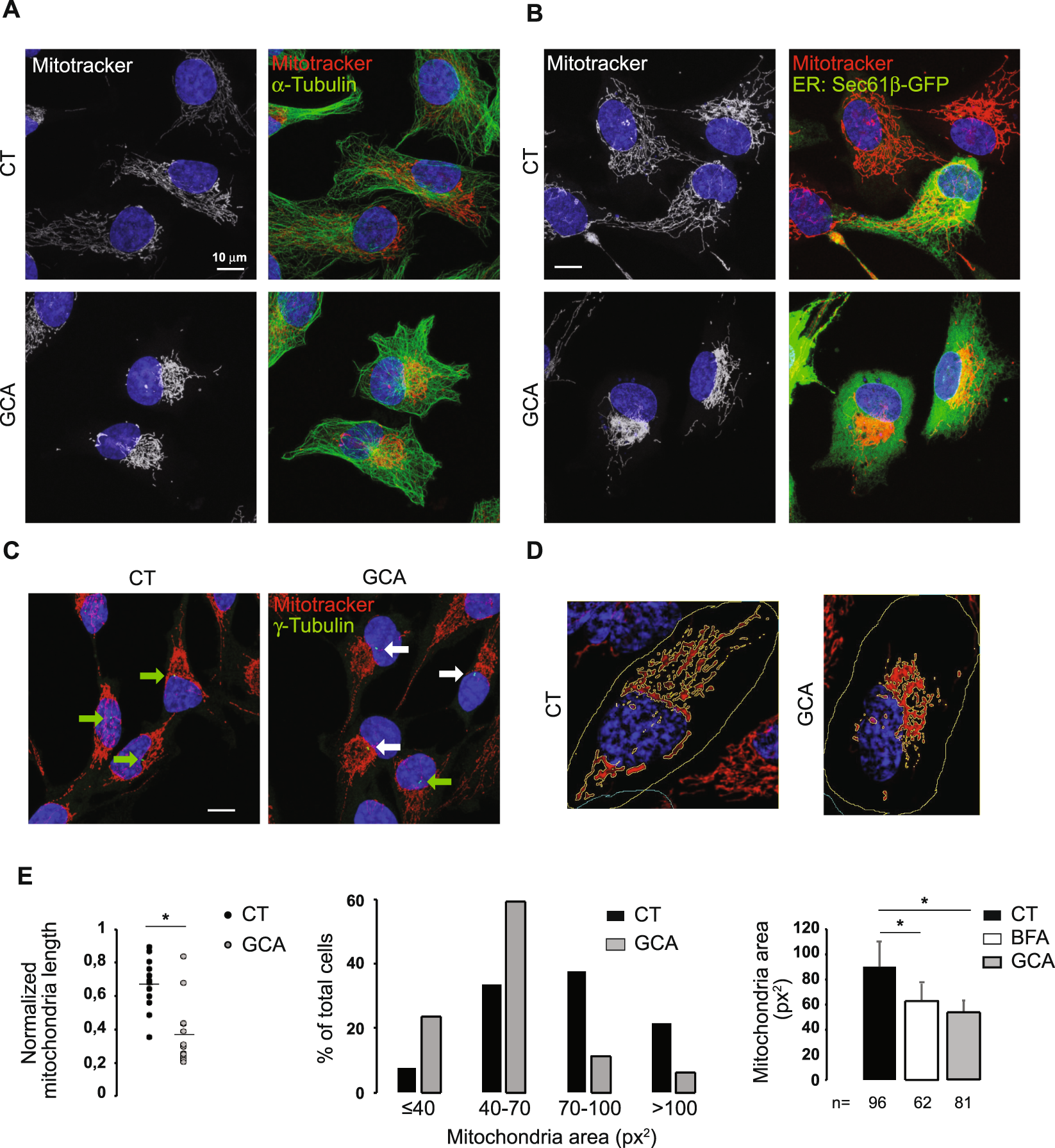
GBF1 and Arf1 interact with Miro and regulate mitochondrial positioning within cells
The GBF1 Sec7 domain directly interacts with the ATGL (300-504) domain
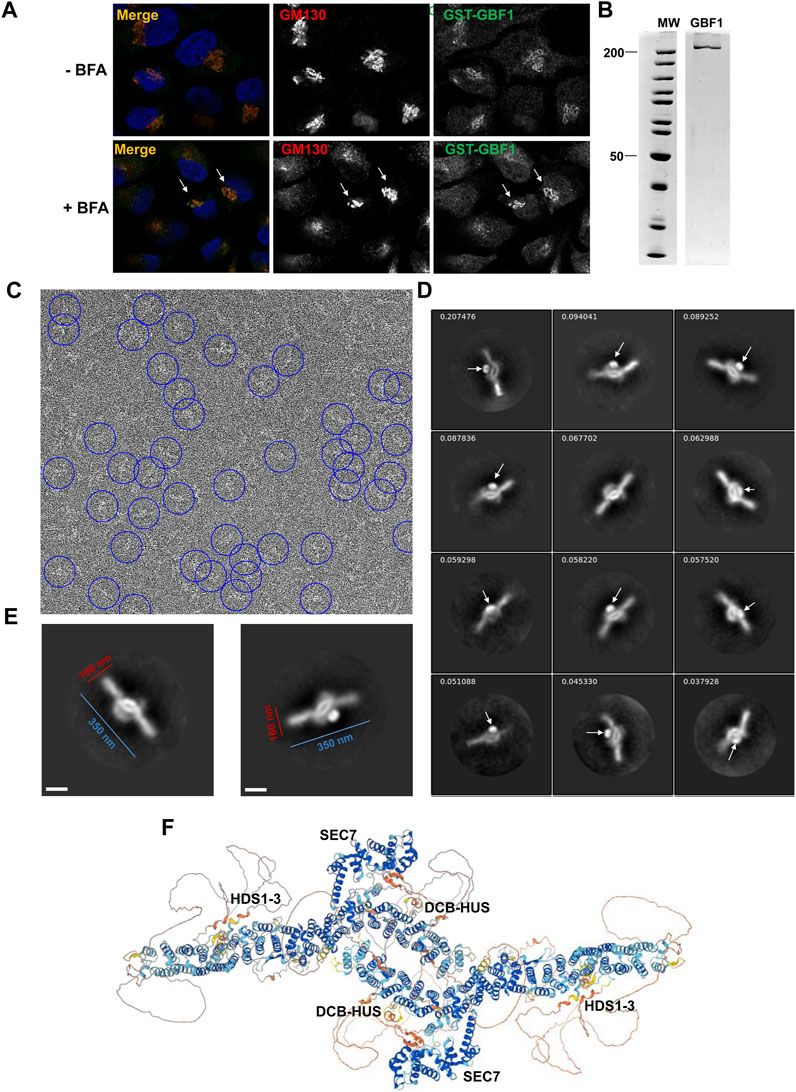
Frontiers The Arf-GEF GBF1 undergoes multi-domain structural shifts to activate Arf at the Golgi
Recomendado para você
-
/i.s3.glbimg.com/v1/AUTH_08fbf48bc0524877943fe86e43087e7a/internal_photos/bs/2023/s/B/9jXiguRQS3Inm7ZcrJAQ/captura-de-tela-2023-02-17-as-17.33.46.png) Friv, Poki e mais: veja 8 sites com jogos online sem precisar baixar28 dezembro 2024
Friv, Poki e mais: veja 8 sites com jogos online sem precisar baixar28 dezembro 2024 -
 FRIV OLD MENU - Old Friv Unblocked Games28 dezembro 2024
FRIV OLD MENU - Old Friv Unblocked Games28 dezembro 2024 -
 How to play FRIV OLD MENU in 2022 - Friv Xmas, Friv Late Night Games, Friv Deleted Games List28 dezembro 2024
How to play FRIV OLD MENU in 2022 - Friv Xmas, Friv Late Night Games, Friv Deleted Games List28 dezembro 2024 -
 Friv 2017 Free Premium Games [Juegos28 dezembro 2024
Friv 2017 Free Premium Games [Juegos28 dezembro 2024 -
 Friv Games APK Download 2023 - Free - 9Apps28 dezembro 2024
Friv Games APK Download 2023 - Free - 9Apps28 dezembro 2024 -
 friv legend.c28 dezembro 2024
friv legend.c28 dezembro 2024 -
 FRIV-Tastic Games! - APK Download for Android28 dezembro 2024
FRIV-Tastic Games! - APK Download for Android28 dezembro 2024 -
 WORD SEARCH - FUN PUZZLE GAMES - Friv 2019 Games28 dezembro 2024
WORD SEARCH - FUN PUZZLE GAMES - Friv 2019 Games28 dezembro 2024 -
 The ancient Thracian endemic plant Haberlea rhodopensis Friv. and related species: A review - ScienceDirect28 dezembro 2024
The ancient Thracian endemic plant Haberlea rhodopensis Friv. and related species: A review - ScienceDirect28 dezembro 2024 -
 Power Pamplona, Working, No Ads28 dezembro 2024
Power Pamplona, Working, No Ads28 dezembro 2024
você pode gostar
-
 Should You See a Ping Pong Show in Bangkok? - Hippie In Heels28 dezembro 2024
Should You See a Ping Pong Show in Bangkok? - Hippie In Heels28 dezembro 2024 -
 How to Fix The Last of Us Part 1 PC Texture Not Loading - The Panther Tech28 dezembro 2024
How to Fix The Last of Us Part 1 PC Texture Not Loading - The Panther Tech28 dezembro 2024 -
 Puzzle+Jogo - Descobrir o Mundo28 dezembro 2024
Puzzle+Jogo - Descobrir o Mundo28 dezembro 2024 -
 Cube Mission - Play it Online at Coolmath Games28 dezembro 2024
Cube Mission - Play it Online at Coolmath Games28 dezembro 2024 -
 Play Taming.io Free Online Games. KidzSearch.com28 dezembro 2024
Play Taming.io Free Online Games. KidzSearch.com28 dezembro 2024 -
 Google Doodle Champion Island Videos - Page 28 of 8828 dezembro 2024
Google Doodle Champion Island Videos - Page 28 of 8828 dezembro 2024 -
 Swing Fanatics - Your Love Is A Lie MP3 Download & Lyrics28 dezembro 2024
Swing Fanatics - Your Love Is A Lie MP3 Download & Lyrics28 dezembro 2024 -
 Ayanokoji28 dezembro 2024
Ayanokoji28 dezembro 2024 -
 John Doe, jogue online no PokerStars Casino28 dezembro 2024
John Doe, jogue online no PokerStars Casino28 dezembro 2024 -
 How to Download Killer in Purple 2 on Android? - Mobile Updates28 dezembro 2024
How to Download Killer in Purple 2 on Android? - Mobile Updates28 dezembro 2024