Solved Exercise \#2: Suppose we have a random variable X
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 02 abril 2025

Answer to Solved Exercise \#2: Suppose we have a random variable X
5.4: The Exponential Distribution - Statistics LibreTexts
Python: Takes two lists and returns True if they have at least one common member - w3resource

Dice: Finding Expected Values of Games of Chance - Video & Lesson Transcript

A Single Population Mean using the Normal Distribution
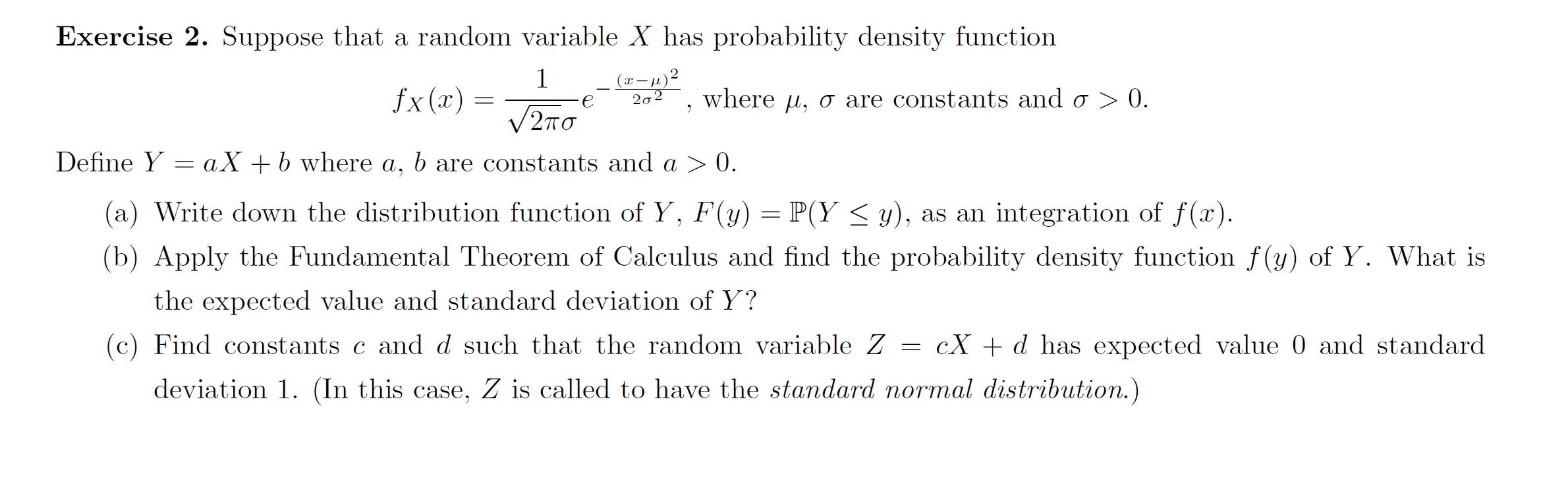
Solved Exercise 2. Suppose that a random variable X has

4.2: Continuous Conditional Probability - Statistics LibreTexts

NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 12 Maths Chapter 13 Probability - Access free PDF

NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 12 Maths Chapter 13 Probability - Access free PDF
How To Find Critical Value In Statistics

If the range of a random variable X is 0,1,2,3, with P(X=k)=(k+1)a3k k≥0, then a=

Bernoulli Distribution - Definition, Formula, Graph, Examples
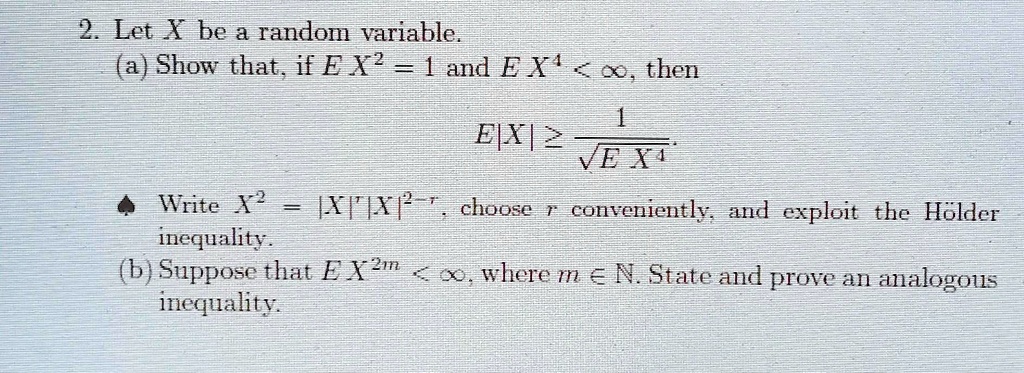
SOLVED: Help me solve this exercise. 2 Let X be a random variable. (a) Show that if E[X] = 1 and E[X'] < ∞, then E[, X

The Binomial Distribution Explained, by Maike Elisa

SOLVED: Exercise: Suppose that a random variable X is observed under two mutually exclusive conditions Ho and Hz with Pr(Ho) + Pr(Hz) = 1. Suppose also that the conditional probability density functions
Recomendado para você
-
 Will you? : r/MinecraftMemes02 abril 2025
Will you? : r/MinecraftMemes02 abril 2025 -
I'd push it #fyp #canadadrew #foryou #viral #funnyvideos #funny #meme02 abril 2025
-
 Will You Press the Button Mike? PUSH IT02 abril 2025
Will You Press the Button Mike? PUSH IT02 abril 2025 -
 Switch Pushbutton Switches Waterproof Switch Button 220v - 16/19/22mm Metal Push - Aliexpress02 abril 2025
Switch Pushbutton Switches Waterproof Switch Button 220v - 16/19/22mm Metal Push - Aliexpress02 abril 2025 -
 POINTERTECK Musical Baby Toys 6 to 12 Months, Baby Piano Light Up Animal Musical Toys for Toddlers 1-3, Infant Kids Learning Toys for 1 Year Old Girl Boy, Baby Toys 12-18 Months Gifts02 abril 2025
POINTERTECK Musical Baby Toys 6 to 12 Months, Baby Piano Light Up Animal Musical Toys for Toddlers 1-3, Infant Kids Learning Toys for 1 Year Old Girl Boy, Baby Toys 12-18 Months Gifts02 abril 2025 -
 Vill you press the button? You can inime enter any BUT You cock can on never02 abril 2025
Vill you press the button? You can inime enter any BUT You cock can on never02 abril 2025 -
 Lesson 18 Control an LED with a Button02 abril 2025
Lesson 18 Control an LED with a Button02 abril 2025 -
 Intro To Electronics for Kids: 03 Digital LED Button02 abril 2025
Intro To Electronics for Kids: 03 Digital LED Button02 abril 2025 -
Solved 4. You arrive into a building and are about to take02 abril 2025
-
 Powered Online Survey02 abril 2025
Powered Online Survey02 abril 2025
você pode gostar
-
![Assassin's Icon Valhalla [Assassin's Creed] - Assassins Creed - T-Shirt sold by Ivan Chan, SKU 1871783](https://cdn.printerval.com/unsafe/960x960/assets.printerval.com/2023/11/04/20231104124429-P1871783-MEN-HET-M-BLA-238-assassin-39-s-icon-valhalla-assassin-39-s-creed-assassins-creed-t-shirt.jpg) Assassin's Icon Valhalla [Assassin's Creed] - Assassins Creed - T-Shirt sold by Ivan Chan, SKU 187178302 abril 2025
Assassin's Icon Valhalla [Assassin's Creed] - Assassins Creed - T-Shirt sold by Ivan Chan, SKU 187178302 abril 2025 -
 The Rock, DifficultyRPG Wiki02 abril 2025
The Rock, DifficultyRPG Wiki02 abril 2025 -
 Redutores, Motorredutores, Motores elétricos WEG - Transmitech Redutores02 abril 2025
Redutores, Motorredutores, Motores elétricos WEG - Transmitech Redutores02 abril 2025 -
 Anime Warriors codes (December 2023) — free yen, boosts and02 abril 2025
Anime Warriors codes (December 2023) — free yen, boosts and02 abril 2025 -
 Dragon Ball Super: Broly confirma um importante detalhe sobre a origem de Goku - Critical Hits02 abril 2025
Dragon Ball Super: Broly confirma um importante detalhe sobre a origem de Goku - Critical Hits02 abril 2025 -
 Anime War Tycoon codes (October 2023) - Free boosts and yen02 abril 2025
Anime War Tycoon codes (October 2023) - Free boosts and yen02 abril 2025 -
 SPORTS PREDICTION FOR TOMORROW GAME (27 Sep) #sportspredictions02 abril 2025
SPORTS PREDICTION FOR TOMORROW GAME (27 Sep) #sportspredictions02 abril 2025 -
 Blocos de montar pecas grandes02 abril 2025
Blocos de montar pecas grandes02 abril 2025 -
 Forza horizon 2 Xbox 360 : r/forza02 abril 2025
Forza horizon 2 Xbox 360 : r/forza02 abril 2025 -
Squid Game: The Challenge' Winner Must Play The Waiting Game To Get $4.5 Million Prize02 abril 2025


