Size Dependence of Liquid–Liquid Phase Separation by in Situ Study of Flowing Submicron Aerosol Particles
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 26 janeiro 2025


Evidence for a semisolid phase state of aerosols and droplets relevant to the airborne and surface survival of pathogens

Aerosol Optical Tweezers Constrain the Morphology Evolution of Liquid-Liquid Phase-Separated Atmospheric Particles - ScienceDirect

Evidence for a semisolid phase state of aerosols and droplets relevant to the airborne and surface survival of pathogens

Size Dependence of Liquid–Liquid Phase Separation by in Situ Study of Flowing Submicron Aerosol Particles

Toward a molecular understanding of the surface composition of atmospherically relevant organic particles
The physics of respiratory particle generation, fate in the air, and inhalation

Measurements of Aerosol Particle Size Distributions and INPs Over the Southern Ocean in the Late Austral Summer of 2017 on Board the R/V Mirai: Importance of the Marine Boundary Layer Structure
Hygroscopic growth of single atmospheric sea salt aerosol particles from mass measurement in an optical trap - Environmental Science: Atmospheres (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/D2EA00129B
Frontiers Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation: Unraveling the Enigma of Biomolecular Condensates in Microbial Cells
Atmosphere, Free Full-Text

Menthol in electronic cigarettes causes biophysical inhibition of pulmonary surfactant
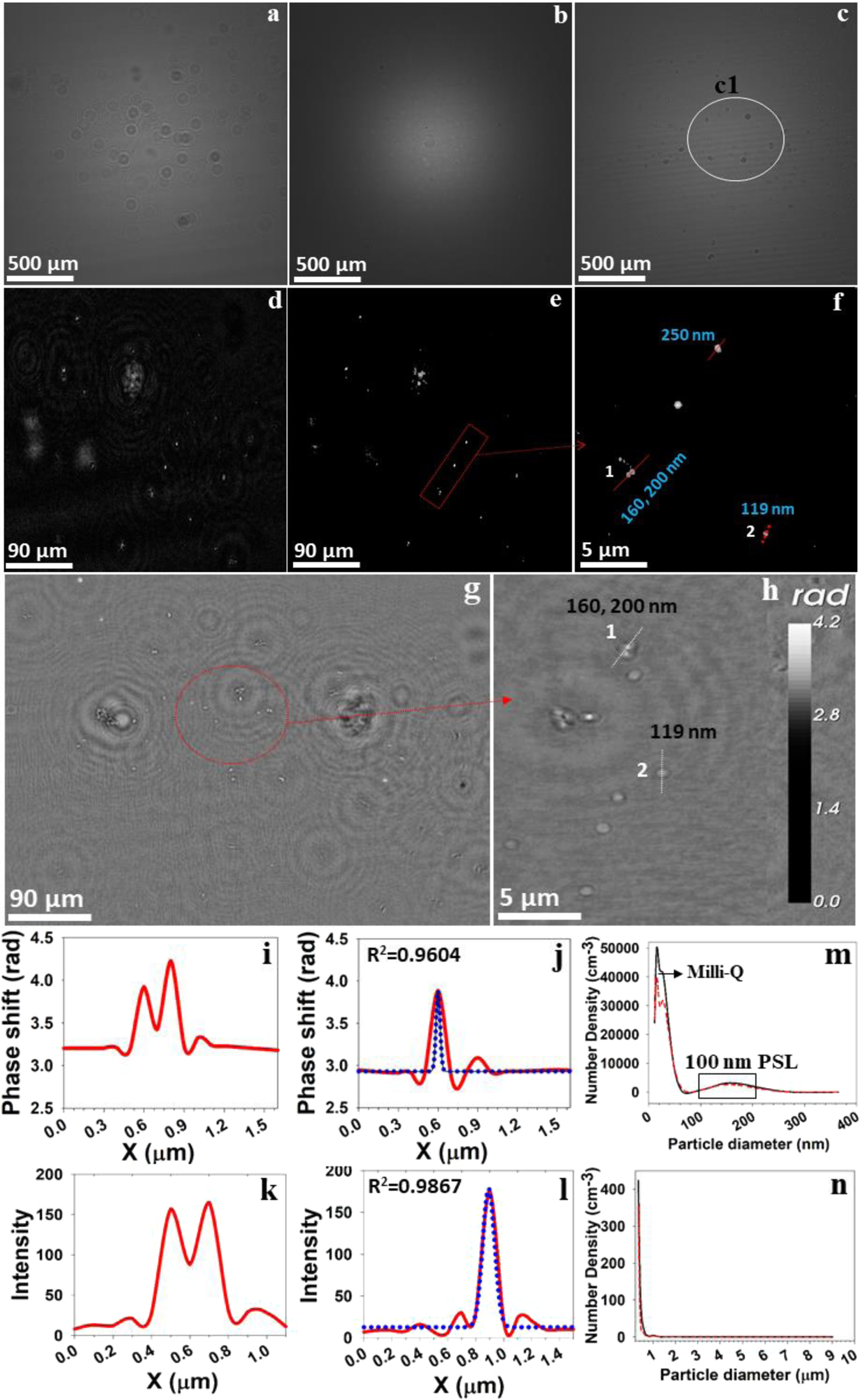
Advancing the science of dynamic airborne nanosized particles using Nano-DIHM

How liquid–liquid phase separation induces active spreading
Visual Evidence That Atmospheric Particles Can Undergo Liquid–Liquid Phase Separations
AMT - Flow-induced errors in airborne in situ measurements of aerosols and clouds
Recomendado para você
-
 Stream Gore Funkin OST - MDPOPE V2 by Josh Boss 326 janeiro 2025
Stream Gore Funkin OST - MDPOPE V2 by Josh Boss 326 janeiro 2025 -
 ACP - Biomass burning and marine aerosol processing over the southeast Atlantic Ocean: a TEM single-particle analysis26 janeiro 2025
ACP - Biomass burning and marine aerosol processing over the southeast Atlantic Ocean: a TEM single-particle analysis26 janeiro 2025 -
 Exploring the Nanostructures Accessible to an Organic Surfactant Atmospheric Aerosol Proxy26 janeiro 2025
Exploring the Nanostructures Accessible to an Organic Surfactant Atmospheric Aerosol Proxy26 janeiro 2025 -
 Animals, Free Full-Text26 janeiro 2025
Animals, Free Full-Text26 janeiro 2025 -
MDPOPE Play on Anghami26 janeiro 2025
-
MDPOPE - GOD SCREAMS OUT26 janeiro 2025
-
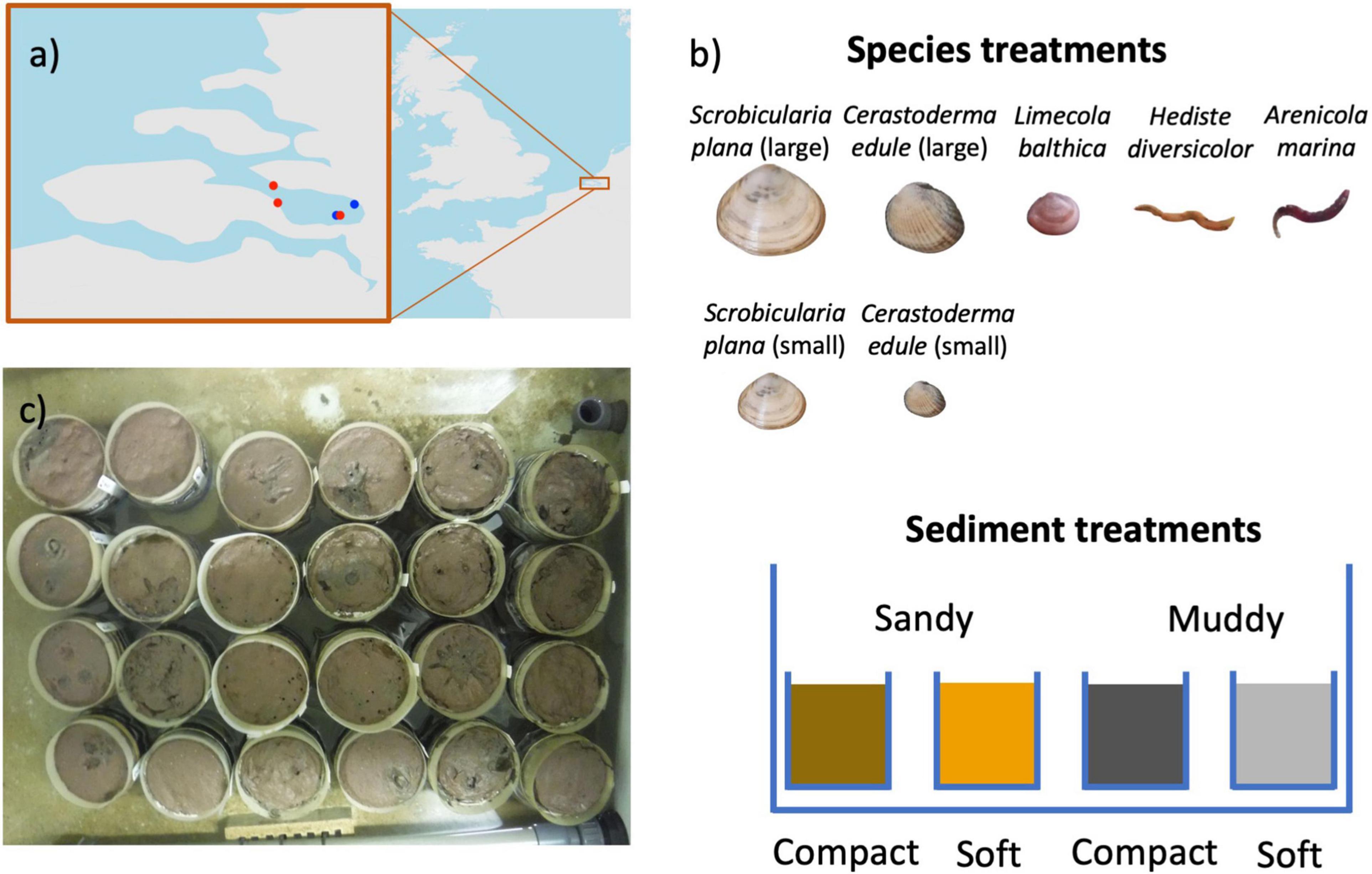 Frontiers Sediment Bulk Density Effects on Benthic Macrofauna Burrowing and Bioturbation Behavior26 janeiro 2025
Frontiers Sediment Bulk Density Effects on Benthic Macrofauna Burrowing and Bioturbation Behavior26 janeiro 2025 -
 Aerosol Mixing State: Measurements, Modeling, and Impacts - Riemer - 2019 - Reviews of Geophysics - Wiley Online Library26 janeiro 2025
Aerosol Mixing State: Measurements, Modeling, and Impacts - Riemer - 2019 - Reviews of Geophysics - Wiley Online Library26 janeiro 2025 -
![Exploring the role of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in fibroblast-like synovial cells in rheumatoid arthritis [PeerJ]](https://dfzljdn9uc3pi.cloudfront.net/2021/11973/1/fig-5-full.png) Exploring the role of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in fibroblast-like synovial cells in rheumatoid arthritis [PeerJ]26 janeiro 2025
Exploring the role of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in fibroblast-like synovial cells in rheumatoid arthritis [PeerJ]26 janeiro 2025 -
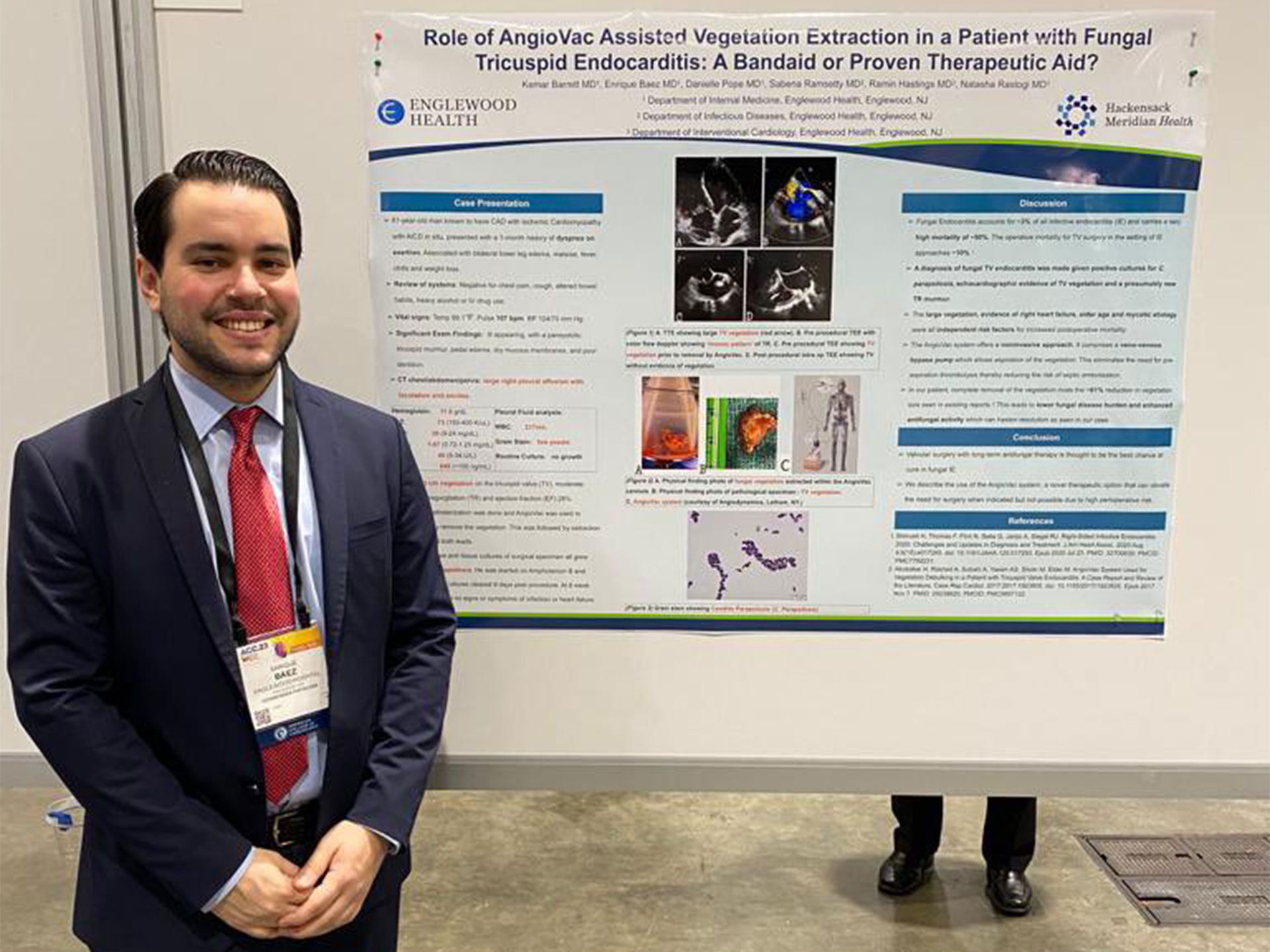 Resident Life - Internal Medicine Residency Program - Englewood Health26 janeiro 2025
Resident Life - Internal Medicine Residency Program - Englewood Health26 janeiro 2025
você pode gostar
-
 Naruto and Sasuke vs. Naruto and Sasuke vs. Naruto and Sasuke - Battles - Comic Vine26 janeiro 2025
Naruto and Sasuke vs. Naruto and Sasuke vs. Naruto and Sasuke - Battles - Comic Vine26 janeiro 2025 -
![Stream Yeast Listen to Reborn killer [SCP-076-2] playlist online](https://i1.sndcdn.com/artworks-qt61nSOl67fmKnrC-vFoQTg-t500x500.jpg) Stream Yeast Listen to Reborn killer [SCP-076-2] playlist online26 janeiro 2025
Stream Yeast Listen to Reborn killer [SCP-076-2] playlist online26 janeiro 2025 -
GitHub - Imperial39/bloxflip-predictor26 janeiro 2025
-
 Who is Iñaki Godoy dating? - Iñaki Godoy: Age, height and facts about One Piece - PopBuzz26 janeiro 2025
Who is Iñaki Godoy dating? - Iñaki Godoy: Age, height and facts about One Piece - PopBuzz26 janeiro 2025 -
Podes tocar em mim Senhor, podes curar a minha Dor, podes viver em mim Senhor! 🎼🎤🙌🏻🔥🙏🏻 #CorpoSanto Fátima Souza, By Nessah Dias26 janeiro 2025
-
 Mortal Kombat 1: DLCs vazados incluem Pacificador e mais26 janeiro 2025
Mortal Kombat 1: DLCs vazados incluem Pacificador e mais26 janeiro 2025 -
 O que são os Jogos dos Povos Indígenas?26 janeiro 2025
O que são os Jogos dos Povos Indígenas?26 janeiro 2025 -
 Yagami Kazuma fanart by YamiKazu on DeviantArt26 janeiro 2025
Yagami Kazuma fanart by YamiKazu on DeviantArt26 janeiro 2025 -
 Pokemon Type Combination Frequencies, Updated for Generation 726 janeiro 2025
Pokemon Type Combination Frequencies, Updated for Generation 726 janeiro 2025 -
 G1 - Conheça games que tem Papai Noel como personagem - notícias em Natal e Ano Novo 201326 janeiro 2025
G1 - Conheça games que tem Papai Noel como personagem - notícias em Natal e Ano Novo 201326 janeiro 2025
