Cureus, Whole-Exome Sequencing Identified a Novel DYRK1A Variant in a Patient With Intellectual Developmental Disorder, Autosomal Dominant 7
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 28 fevereiro 2025
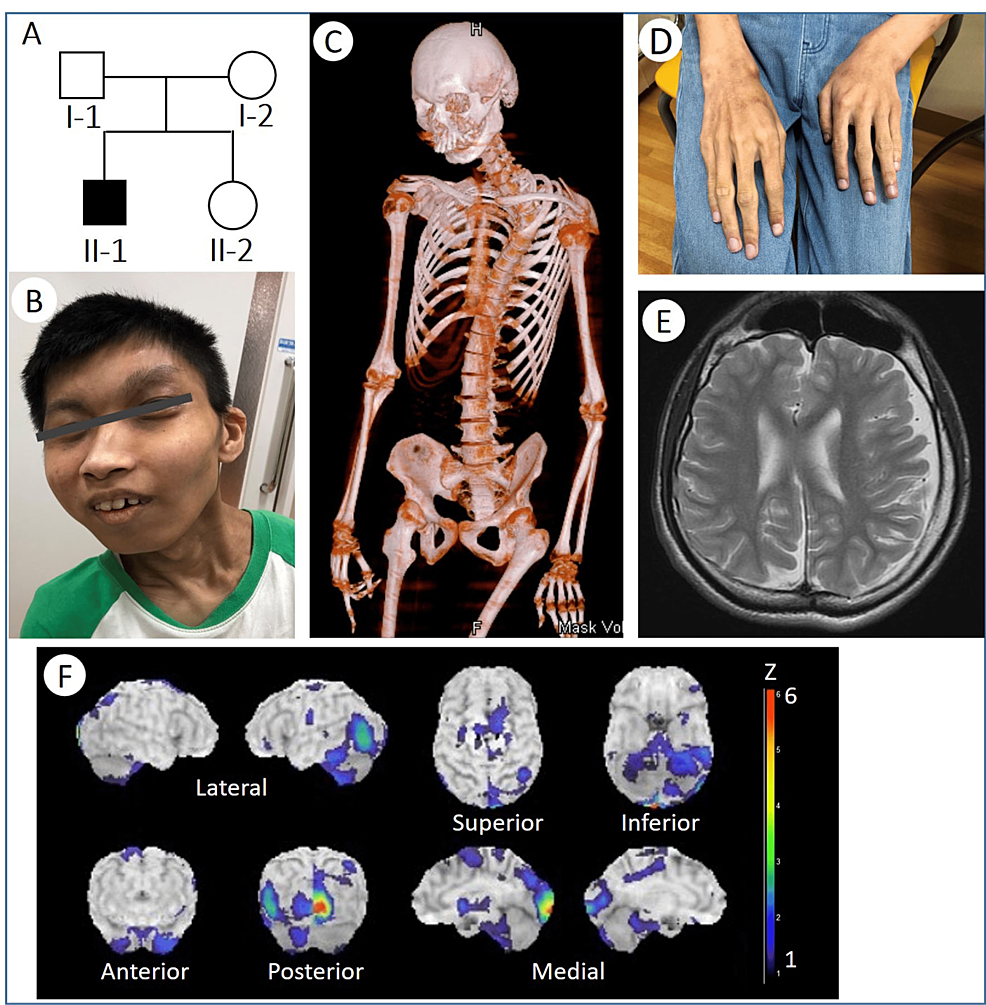
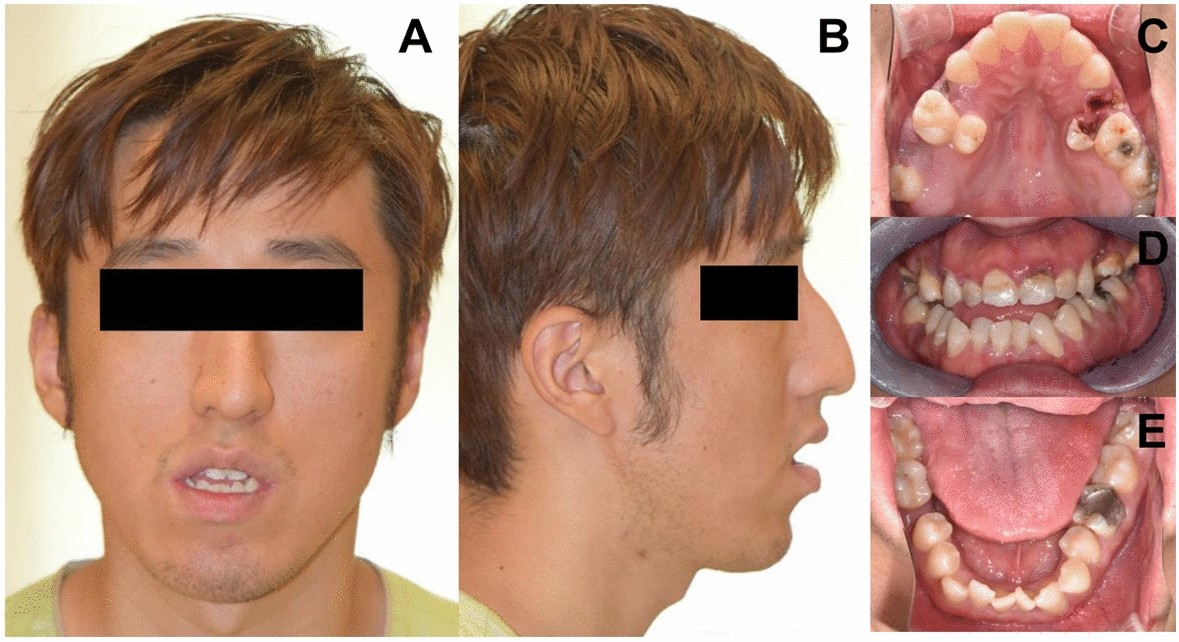
Intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal dominant 7 (MRD7; OMIM 614104) is a rare disease characterized by microcephaly, intellectual disability, speech delay, feeding difficulties, and facial dysmorphisms. This disorder is caused by pathogenic/likely pathogenic variants of the DYRK1A gene, which encodes dual-specificity tyrosine-phosphorylation-regulated kinase 1A. Here, we report a case of MRD7 that was diagnosed using Face2Gene and whole-exome sequencing (WES). A 22-year-old man presented with microcephaly, intellectual disability, slender body, long slender fingers, and facial dysmorphisms. He was previously diagnosed with Cornelia de Lange syndrome (CdLS) at four years of age. However, his CdLS clinical diagnostic score was low at 22 years of age. The Face2Gene application introduced several candidate diseases including MRD7. Finally, by utilizing WES and Sanger sequencing analysis of cloned cDNA, we identified a novel heterozygous duplication variant (c.848dup, p.(Asn283LysfsTer6)) in the DYRK1A gene, which introduces a premature stop codon. This report provides more information about the phenotypic spectrum of a young adult patient with MRD7. Face2Gene helped us introduce candidate diseases of the patient. Registering further genetically confirmed cases with MRD7 will improve the accuracy of the diagnostic recommendations in Face2Gene. Moreover, WES is a powerful tool for diagnosing rare genetic diseases, such as MRD7.
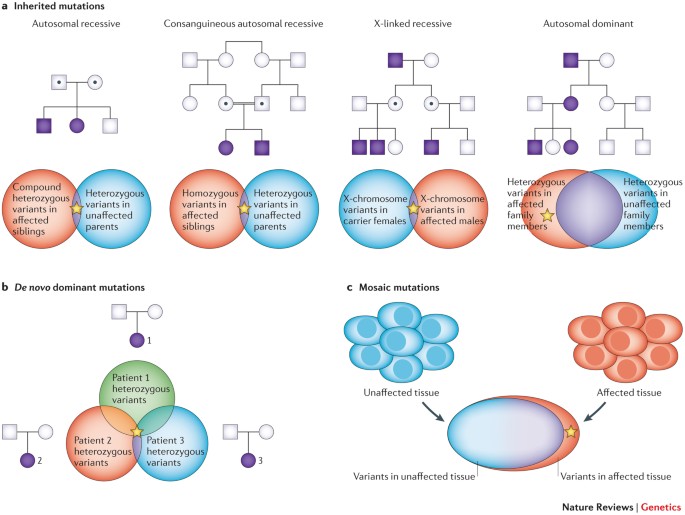
Rare-disease genetics in the era of next-generation sequencing: discovery to translation

PDF) Neurodevelopmental Disorder, Obesity, Pancytopenia, Diabetes Mellitus, Cirrhosis, and Renal Failure in ACBD6 -Associated Syndrome: A Case Report

Integrative approach to interpret DYRK1A variants, leading to a frequent neurodevelopmental disorder

The role of recessive inheritance in early-onset epileptic encephalopathies: a combined whole-exome sequencing and copy number study
Whole exome sequencing identifies a novel intron heterozygous mutation in TSC2 responsible for tuberous sclerosis complex
Pitfalls of whole exome sequencing in undefined clinical conditions with a suspected genetic etiology
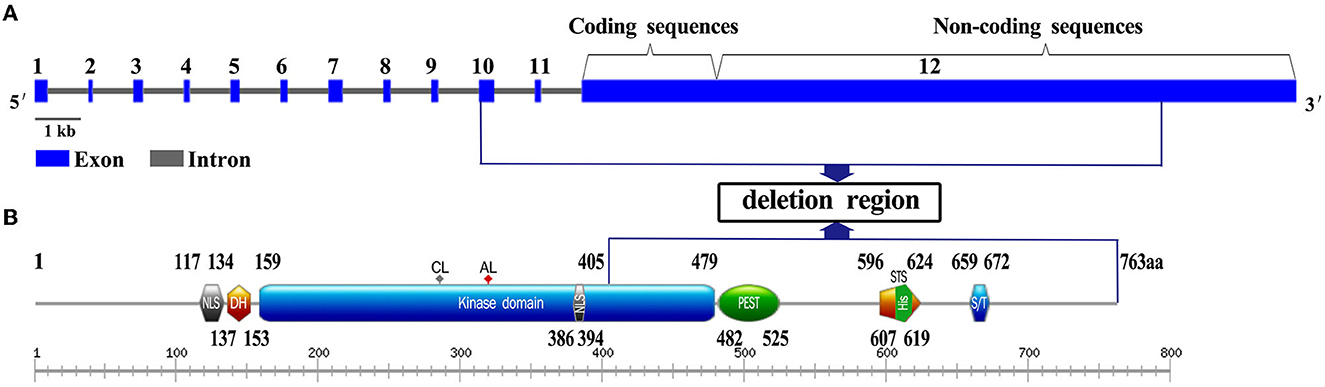
Frontiers Case report: A novel de novo deletion mutation of DYRK1A is associated with intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal dominant 7
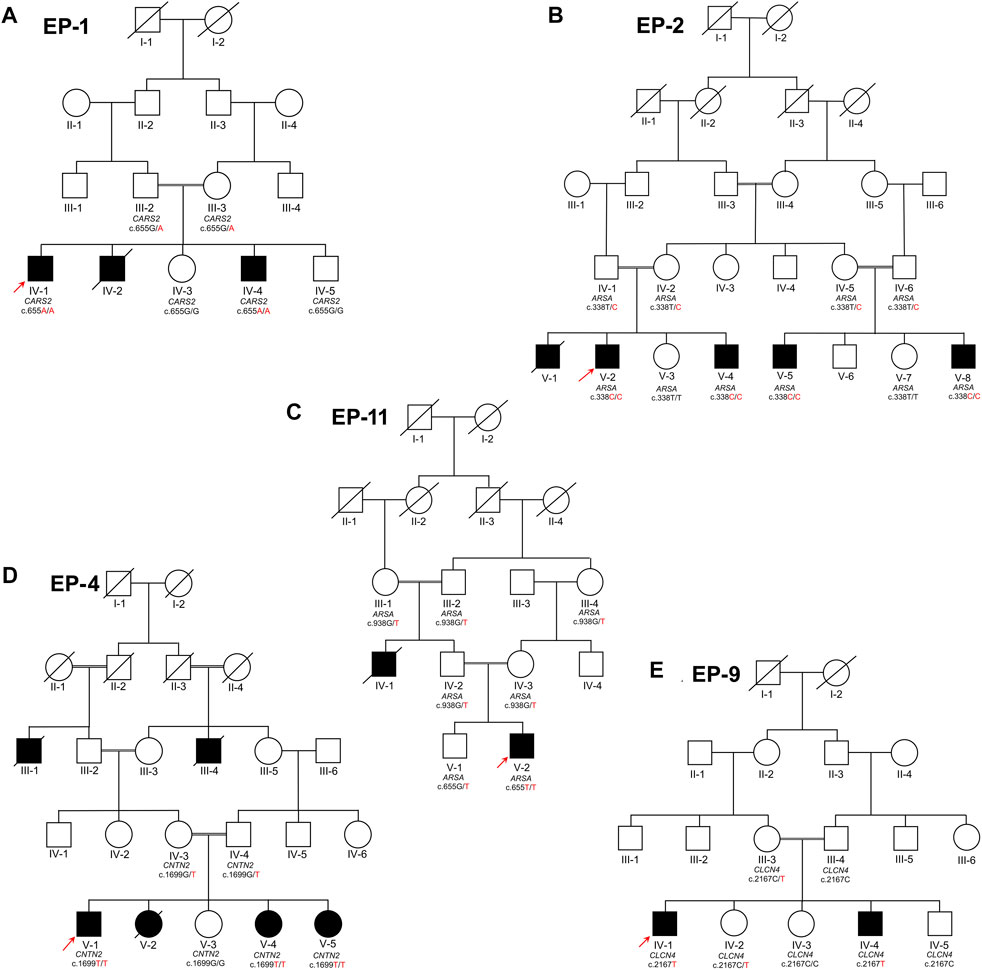
Frontiers Whole exome sequencing identified five novel variants in CNTN2, CARS2, ARSA, and CLCN4 leading to epilepsy in consanguineous families

Clinical Whole-Exome Sequencing for the Diagnosis of Mendelian Disorders
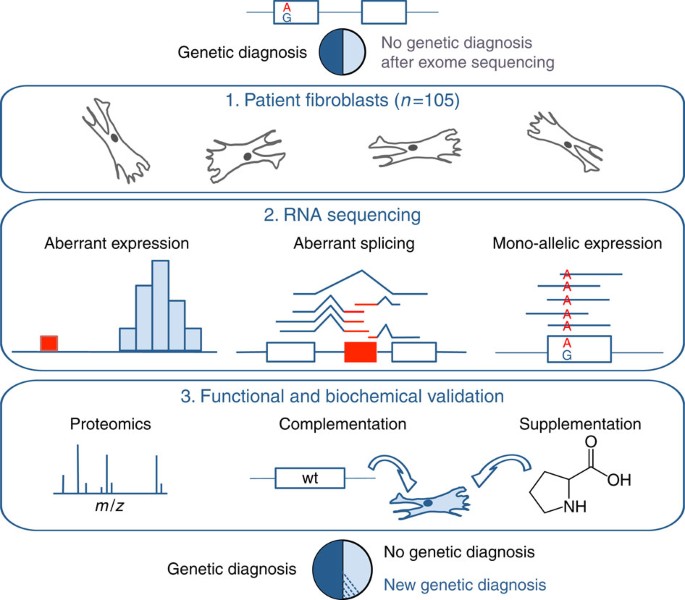
Genetic diagnosis of Mendelian disorders via RNA sequencing

Whole exome sequencing identifies novel DYT1 dystonia-associated genome variants as potential disease modifiers

The contribution of whole-exome sequencing to intellectual disability diagnosis and knowledge of underlying molecular mechanisms: A systematic review and meta-analysis - ScienceDirect

Targeting epigenetics: A novel promise for Alzheimer's disease treatment - ScienceDirect

Autosomal recessive mutations in THOC6 cause intellectual disability: syndrome delineation requiring forward and reverse phenotyping - Amos - 2017 - Clinical Genetics - Wiley Online Library
Recomendado para você
-
 Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome: A Complete Overview — DermNet28 fevereiro 2025
Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome: A Complete Overview — DermNet28 fevereiro 2025 -
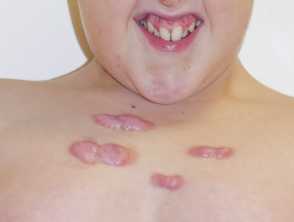
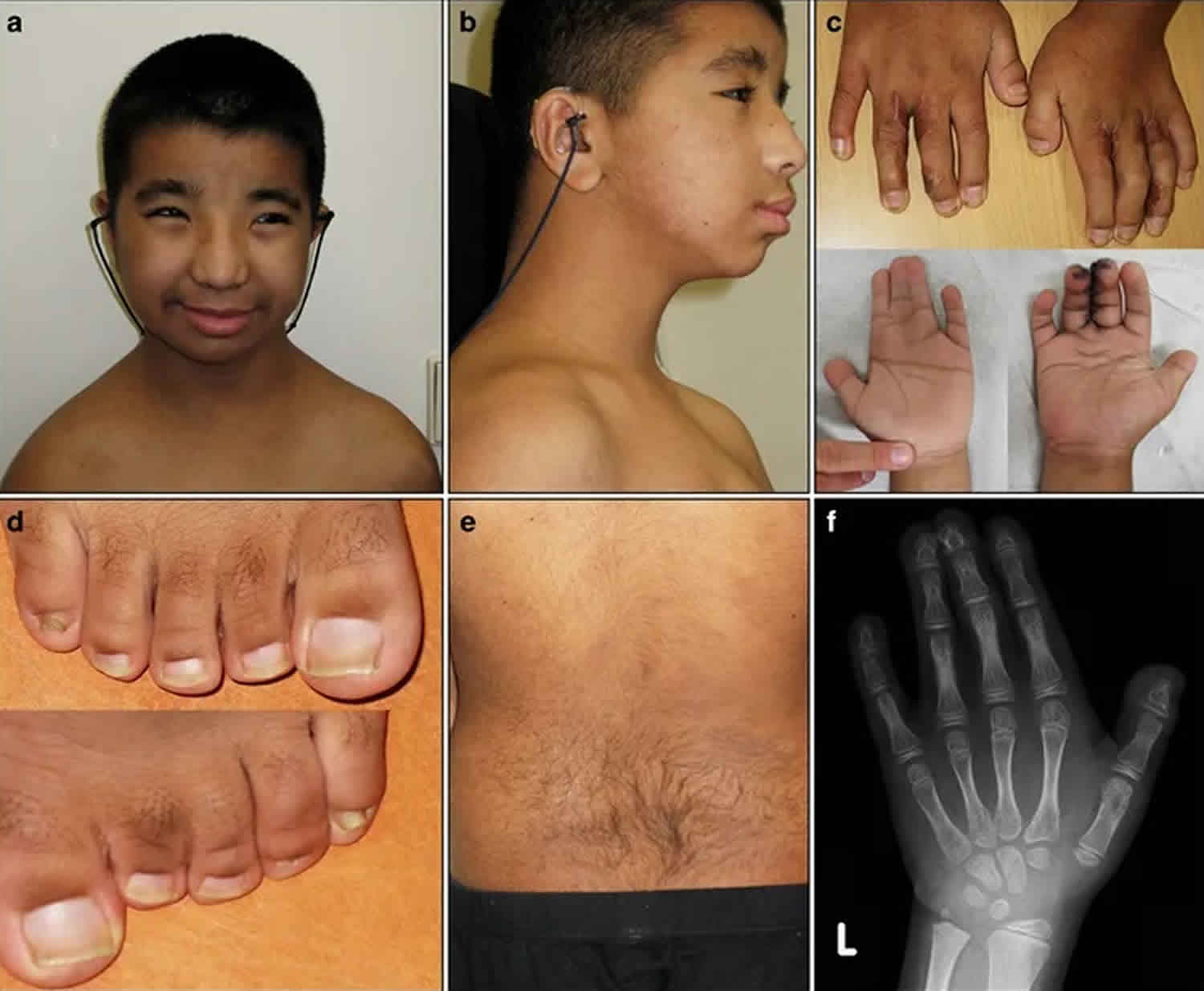
![Figure 2. [Broad terminal phalanges (A) and broad, radially deviated thumbs (B)]. - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1526/bin/rsts-Image002.jpg) Figure 2. [Broad terminal phalanges (A) and broad, radially deviated thumbs (B)]. - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf28 fevereiro 2025
Figure 2. [Broad terminal phalanges (A) and broad, radially deviated thumbs (B)]. - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf28 fevereiro 2025 -
 Rubinstein Taybi syndrome causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment & prognosis28 fevereiro 2025
Rubinstein Taybi syndrome causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment & prognosis28 fevereiro 2025 -
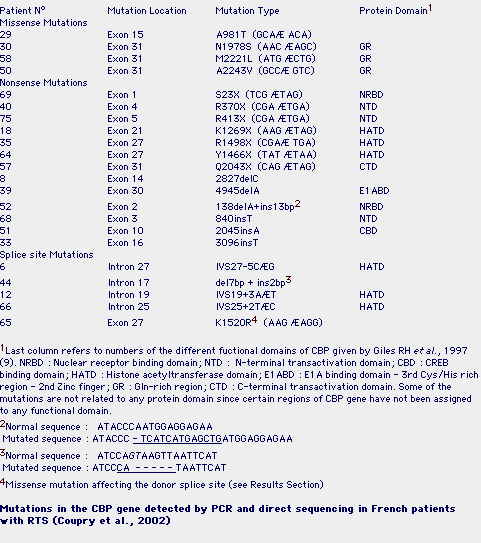
 Genes, Free Full-Text28 fevereiro 2025
Genes, Free Full-Text28 fevereiro 2025 -
 Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome 2 disease: Malacards - Research Articles, Drugs, Genes, Clinical Trials28 fevereiro 2025
Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome 2 disease: Malacards - Research Articles, Drugs, Genes, Clinical Trials28 fevereiro 2025 -
 Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome (RTS)28 fevereiro 2025
Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome (RTS)28 fevereiro 2025 -
 Full article: Psychomotor, cognitive, and socio-emotional developmental profiles of children with Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome and a severe intellectual disability28 fevereiro 2025
Full article: Psychomotor, cognitive, and socio-emotional developmental profiles of children with Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome and a severe intellectual disability28 fevereiro 2025 -
 What is CdLS? Ben and his Brothers: Life with 4 boys and CdLS28 fevereiro 2025
What is CdLS? Ben and his Brothers: Life with 4 boys and CdLS28 fevereiro 2025 -
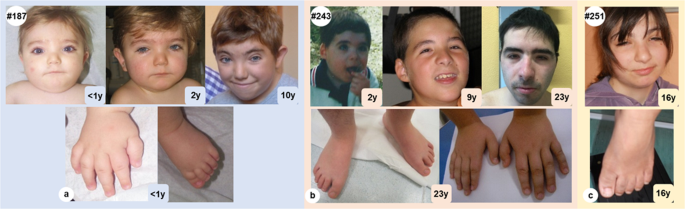 Expanding the phenotype associated to KMT2A variants: overlapping28 fevereiro 2025
Expanding the phenotype associated to KMT2A variants: overlapping28 fevereiro 2025 -
 Identification of de novo EP300 and PLAU variants in a patient28 fevereiro 2025
Identification of de novo EP300 and PLAU variants in a patient28 fevereiro 2025
você pode gostar
-
 The Forbidden Planet Vintage Movie Poster Photograph by Bob Christopher - Fine Art America28 fevereiro 2025
The Forbidden Planet Vintage Movie Poster Photograph by Bob Christopher - Fine Art America28 fevereiro 2025 -
 Resultado de imagem para deus é poderoso para fazer infinitamente mais do que pedimos ou pensamos28 fevereiro 2025
Resultado de imagem para deus é poderoso para fazer infinitamente mais do que pedimos ou pensamos28 fevereiro 2025 -
 Hajime no Ippo - Makunouchi Ippo Manga art, Anime drawings, Anime photo profile dark28 fevereiro 2025
Hajime no Ippo - Makunouchi Ippo Manga art, Anime drawings, Anime photo profile dark28 fevereiro 2025 -
 carrot-kun // おつかれ, ハイステ! on X: Kaze ga Tsuyoku Fuiteiru28 fevereiro 2025
carrot-kun // おつかれ, ハイステ! on X: Kaze ga Tsuyoku Fuiteiru28 fevereiro 2025 -
Map of New Haven Parks 0.5 Mile Buffer Area and Census Block Group Tracts28 fevereiro 2025
-
 Genshin Impact agrada com belos visuais e desafios28 fevereiro 2025
Genshin Impact agrada com belos visuais e desafios28 fevereiro 2025 -
 All about Cristiano Ronaldo dos Santos Aveiro — icenicesea: Cristiano Ronaldo28 fevereiro 2025
All about Cristiano Ronaldo dos Santos Aveiro — icenicesea: Cristiano Ronaldo28 fevereiro 2025 -
 👕, Ideias de roupas para sua OC no Gacha Club, 👕28 fevereiro 2025
👕, Ideias de roupas para sua OC no Gacha Club, 👕28 fevereiro 2025 -
Steam Workshop::King Dice (Cuphead)28 fevereiro 2025
-
 Pokemon - Raikou V GG41/GG70 - Crown Zenith - Galarian Gallery - Ultra Rare Alternate Art : : Brinquedos e Jogos28 fevereiro 2025
Pokemon - Raikou V GG41/GG70 - Crown Zenith - Galarian Gallery - Ultra Rare Alternate Art : : Brinquedos e Jogos28 fevereiro 2025
