Cells, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 01 março 2025
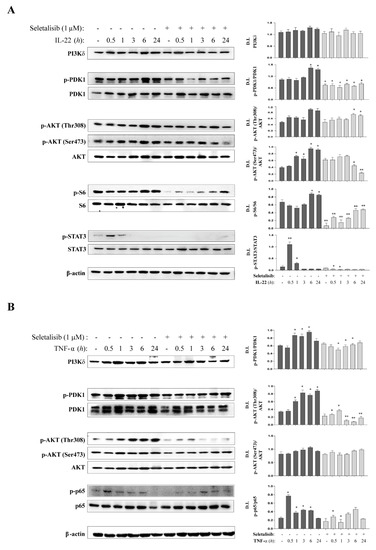
The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)-dependent signaling pathway is aberrantly activated in psoriatic lesions and contributes to disease pathogenesis. Among PI3Ks enzymes, PI3Kα, β, and δ isoforms are known to bind the p85 regulatory subunit and mediate activation of AKT and other downstream effectors. In this study, we deepened our understanding of the expression and function of PI3Kδ in skin lesions of patients affected by psoriasis. For the first time, we found that PI3Kδ is overexpressed in psoriatic plaques, and its expression is not only confined to infiltrating immune cells but also accumulates in proliferating keratinocytes of the epidermal basal layer. We investigated the function of PI3Kδ in psoriatic skin by evaluating the impact of seletalisib, a newly developed selective PI3Kδ inhibitor, in both in vitro and in vivo experimental models of psoriasis. Of note, we found that PI3Kδ sustains keratinocyte hyperproliferation and impaired terminal differentiation induced by IL-22, as well as induces epithelial inflammation and resistance to apoptosis mediated by TNF-α in human keratinocytes. Mechanistically, PI3Kδ promotes PDK1 phosphorylation and signals through AKT-dependent or -independent pathways. It is worth mentioning that PI3Kδ inhibition by seletalisib attenuates the severity of psoriasiform phenotype induced in the Imiquimod-induced mouse model of psoriasis by restoring the physiological proliferation and differentiation programs in epidermal keratinocytes and contrasting the cutaneous inflammatory responses. Therefore, we suggest PI3Kδ as a potential topically druggable target in psoriasis and skin diseases characterized by epidermal hyperproliferation and skin inflammation.
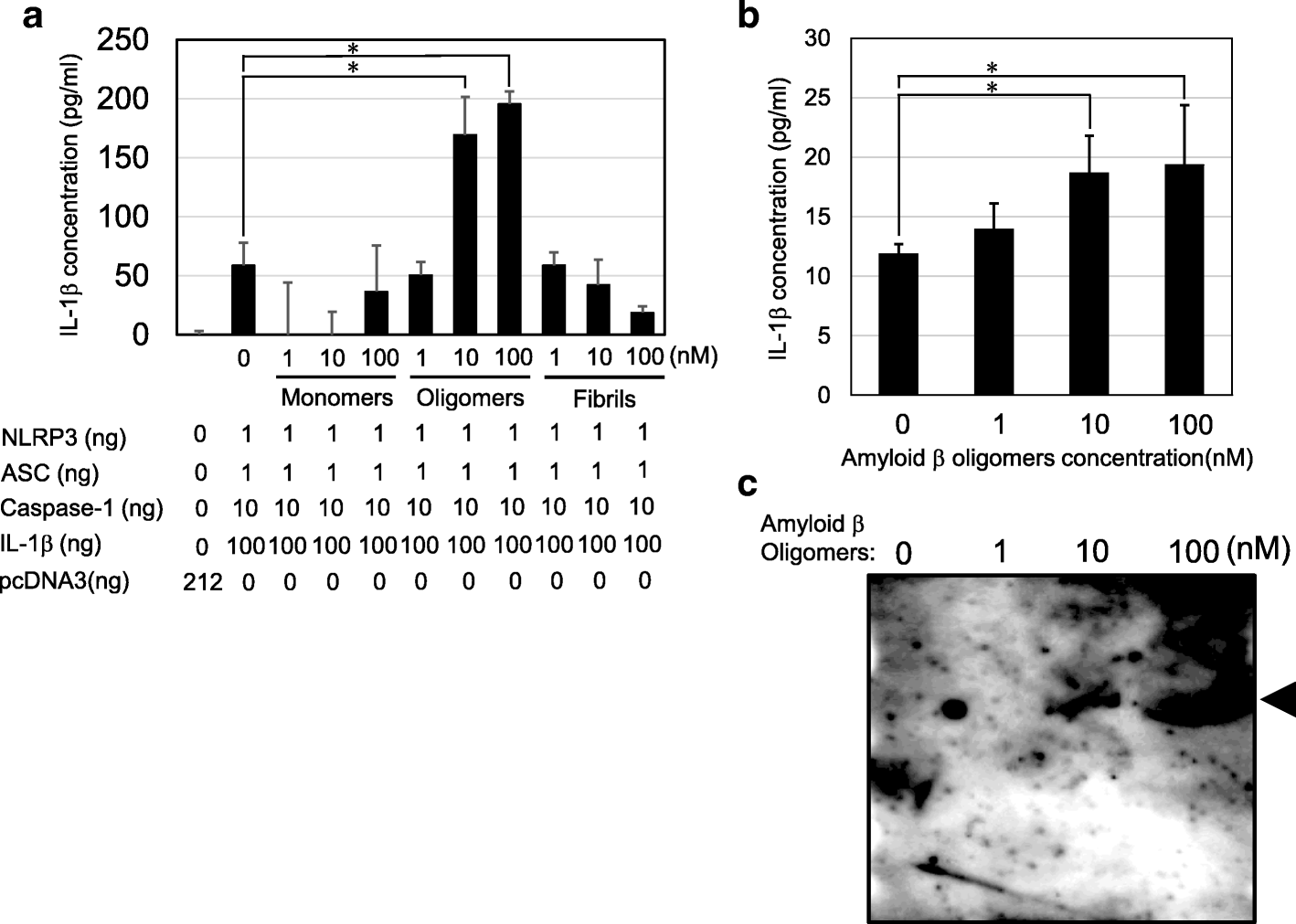
Amyloid β directly interacts with NLRP3 to initiate inflammasome activation: identification of an intrinsic NLRP3 ligand in a cell-free system, Inflammation and Regeneration
The dependence of cell-free protein synthesis in E. coli upon naturally occurring or synthetic polyribonucleotides. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Cells, Free Full-Text

Cell-Free DNA and Apoptosis: How Dead Cells Inform About the Living - ScienceDirect
PDF) Protein structural biology using cell-free platform from wheat germ

Cell-free expression and synthesis of viruses and bacteriophages: applications to medicine and nanotechnology - ScienceDirect

Harnessing Extracellular Vesicles for Regenerative Therapy - Gowing Life
Cell-free synthesis of human interferon. - Abstract - Europe PMC
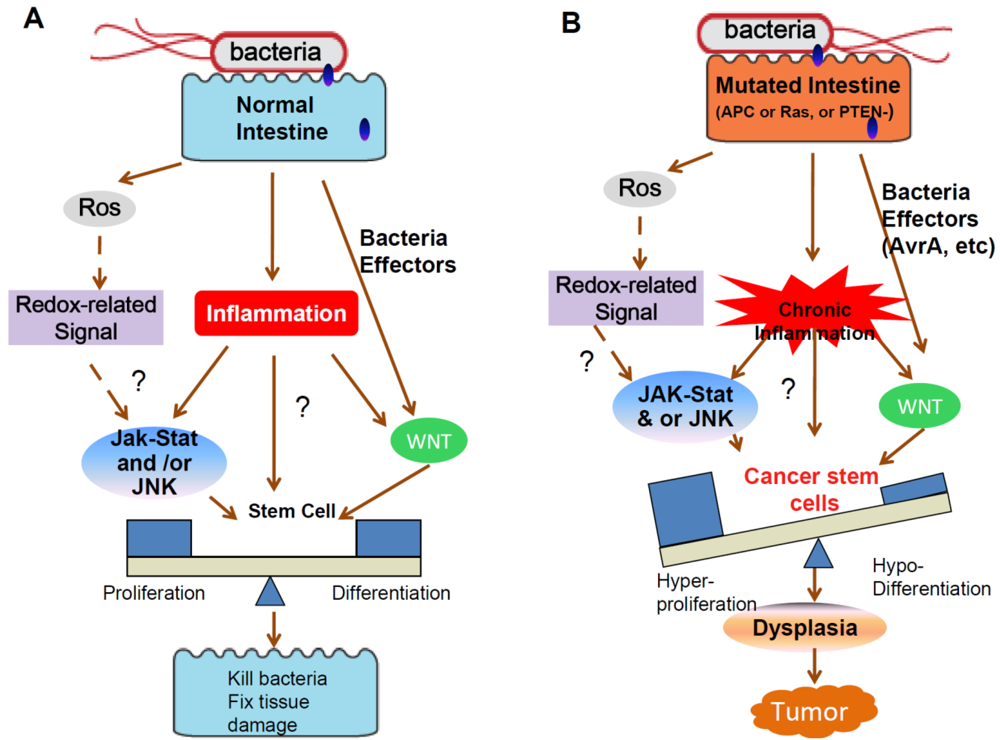
Cancers, Free Full-Text
An illustration of the full-duplex cell-free massive MIMO system.
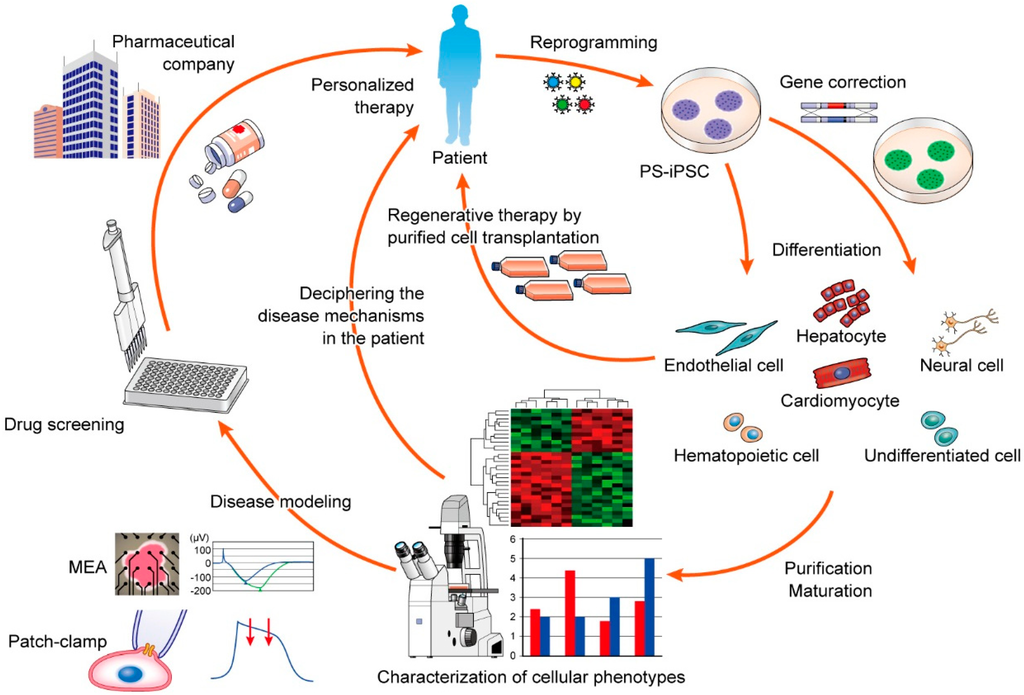
IJMS, Free Full-Text
THE CELL : PAUL REVERE11 : Free Download, Borrow, and Streaming : Internet Archive
Recomendado para você
-
/i.s3.glbimg.com/v1/AUTH_08fbf48bc0524877943fe86e43087e7a/internal_photos/bs/2023/s/B/9jXiguRQS3Inm7ZcrJAQ/captura-de-tela-2023-02-17-as-17.33.46.png) Friv, Poki e mais: veja 8 sites com jogos online sem precisar baixar01 março 2025
Friv, Poki e mais: veja 8 sites com jogos online sem precisar baixar01 março 2025 -
 MINECRAFT REMAKE - Jogue Jogos Friv 2019 Grátis01 março 2025
MINECRAFT REMAKE - Jogue Jogos Friv 2019 Grátis01 março 2025 -
 Poki para Android - Download01 março 2025
Poki para Android - Download01 março 2025 -
 ACTION GAMES 💥 - Play Online Games!01 março 2025
ACTION GAMES 💥 - Play Online Games!01 março 2025 -
 GTA Online - Rockstar Games01 março 2025
GTA Online - Rockstar Games01 março 2025 -
 Poki Mall on the App Store01 março 2025
Poki Mall on the App Store01 março 2025 -
 War of Sticks Walkthrough01 março 2025
War of Sticks Walkthrough01 março 2025 -
 Poki and Fishin' Emotes that were recently unencrypted. (via01 março 2025
Poki and Fishin' Emotes that were recently unencrypted. (via01 março 2025 -
Sem teto??? #streamer #citiesskylines #citiesskylines201 março 2025
-
 JOGOS DE CONSTRUÇÃO 🏗️ - Jogue Grátis Online!01 março 2025
JOGOS DE CONSTRUÇÃO 🏗️ - Jogue Grátis Online!01 março 2025
você pode gostar
-
Body De Bebe Motocross Partiu Trilha Com o Papai01 março 2025
-
 Assistir Genjitsu Shugi Yuusha no Oukoku Saikenki Episódio 9 Online - Animes BR01 março 2025
Assistir Genjitsu Shugi Yuusha no Oukoku Saikenki Episódio 9 Online - Animes BR01 março 2025 -
 33K SCORPION 30K CONDOR ( Starblast.io )01 março 2025
33K SCORPION 30K CONDOR ( Starblast.io )01 março 2025 -
 Adesivo Resinado Desenho Naruto - Sasuke Rezando - Central 6601 março 2025
Adesivo Resinado Desenho Naruto - Sasuke Rezando - Central 6601 março 2025 -
Jogo Do Macaco01 março 2025
-
 RAP MAIS on X: Matuê lança esperada música 'Vampiro' com WIU e01 março 2025
RAP MAIS on X: Matuê lança esperada música 'Vampiro' com WIU e01 março 2025 -
 O PRÓXIMO JOGO GRÁTIS MISTERIOSO da EPIC GAMES STORE, JOGO GRÁTIS na STEAM e JOGOS da SONY no PC!!01 março 2025
O PRÓXIMO JOGO GRÁTIS MISTERIOSO da EPIC GAMES STORE, JOGO GRÁTIS na STEAM e JOGOS da SONY no PC!!01 março 2025 -
 RAINBOW SIX MOBILE IS HERE! HOW TO PLAY ON ANDROID! (NEW GAMEPLAY01 março 2025
RAINBOW SIX MOBILE IS HERE! HOW TO PLAY ON ANDROID! (NEW GAMEPLAY01 março 2025 -
 PS3 Cheats - LEGO Batman 2 DC Super Heroes Guide - IGN01 março 2025
PS3 Cheats - LEGO Batman 2 DC Super Heroes Guide - IGN01 março 2025 -
 Spirit of Unconscious Takamura - Hajime No Ippo - New Challenger on Make a GIF01 março 2025
Spirit of Unconscious Takamura - Hajime No Ippo - New Challenger on Make a GIF01 março 2025


