Cells, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 21 fevereiro 2025
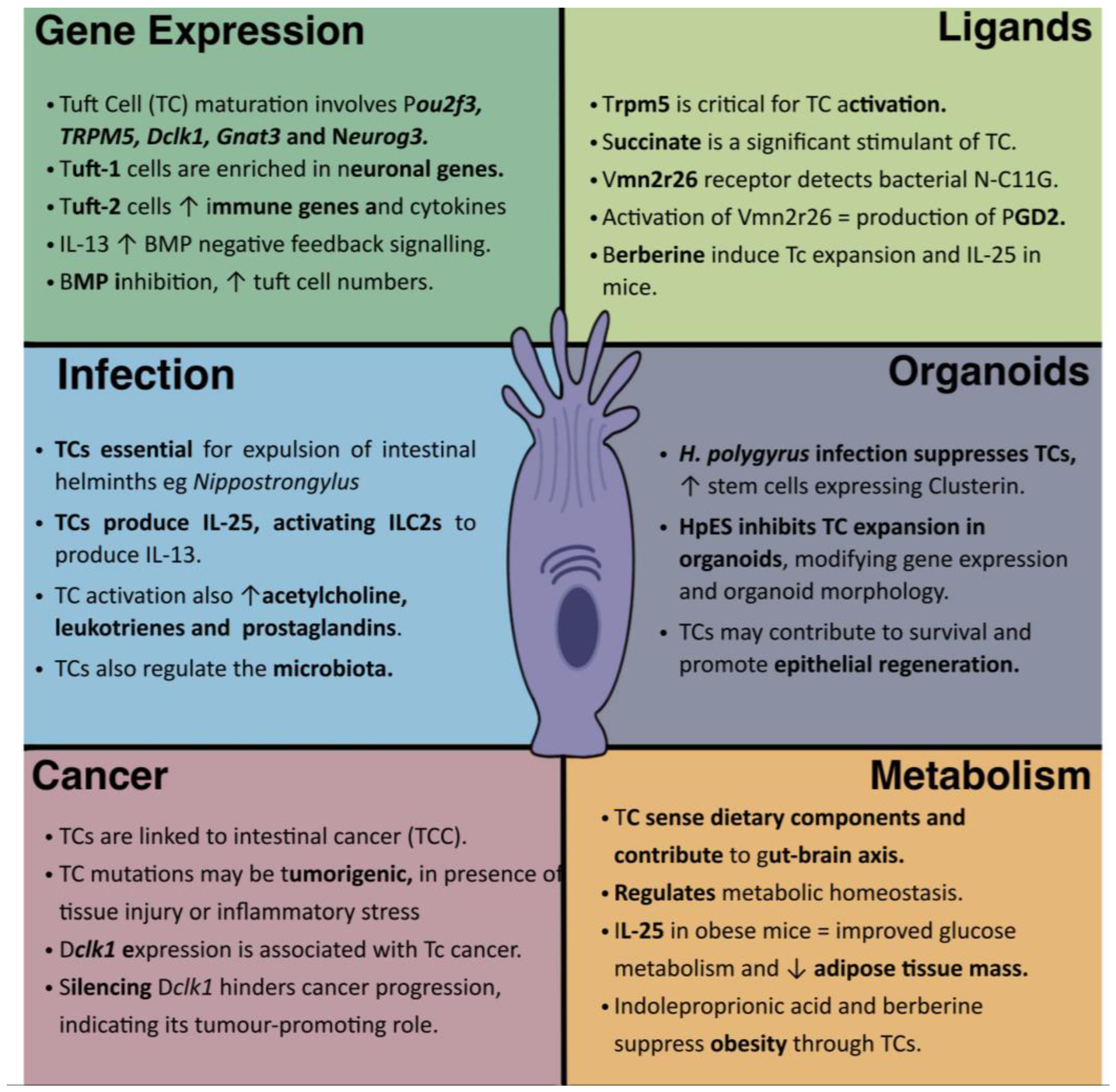
Tuft cells have recently emerged as the focus of intense interest following the discovery of their chemosensory role in the intestinal tract, and their ability to activate Type 2 immune responses to helminth parasites. Moreover, they populate a wide range of mucosal tissues and are intimately connected to immune and neuronal cells, either directly or through the release of pharmacologically active mediators. They are now recognised to fulfil both homeostatic roles, in metabolism and tissue integrity, as well as acting as the first sensors of parasite infection, immunity to which is lost in their absence. In this review we focus primarily on the importance of tuft cells in the intestinal niche, but also link to their more generalised physiological role and discuss their potential as targets for the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders.

Rapid cell-free characterization of multi-subunit CRISPR effectors and transposons - ScienceDirect
An illustration of the full-duplex cell-free massive MIMO system.
IAPP/amylin-induced interaction between NLRP3 and ASC in a cell-free

Cell Circuits and Complex Tissues

Effect of calendar ageing on the cycle life of anode-free full-cells.
Cells, Free Full-Text

The cell-free system: A new apparatus for affordable, sensitive, and portable healthcare - ScienceDirect
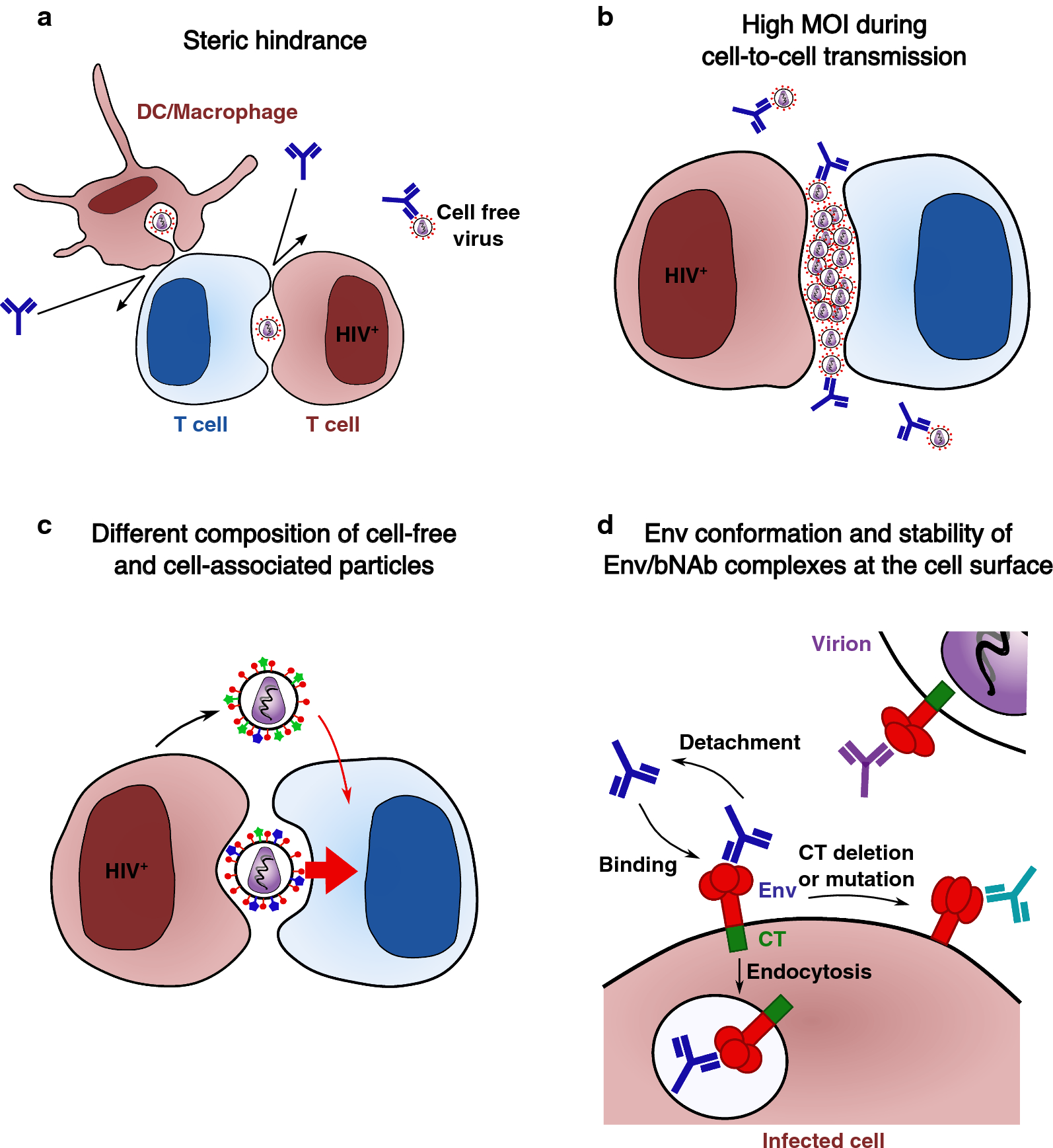
HIV-1 cell-to-cell transmission and broadly neutralizing antibodies, Retrovirology
Full-spectrum cell-free RAN for 6G systems: s
PDF) Protein structural biology using cell-free platform from wheat germ
Recomendado para você
-
 Welcome to League of Legends: Wild Rift21 fevereiro 2025
Welcome to League of Legends: Wild Rift21 fevereiro 2025 -
 Dead Cells: Return To Castlevania - Netflix Edition Gameplay (Android/iOS)21 fevereiro 2025
Dead Cells: Return To Castlevania - Netflix Edition Gameplay (Android/iOS)21 fevereiro 2025 -
 Wild Rift News September 9, 202221 fevereiro 2025
Wild Rift News September 9, 202221 fevereiro 2025 -
 Cell Stage in 04:16 by Savage_Brick - Spore - Speedrun21 fevereiro 2025
Cell Stage in 04:16 by Savage_Brick - Spore - Speedrun21 fevereiro 2025 -
 Wild Rift Patch 3.4b New Content: Vex, Supreme Cells, Bewitching Skins and More21 fevereiro 2025
Wild Rift Patch 3.4b New Content: Vex, Supreme Cells, Bewitching Skins and More21 fevereiro 2025 -
 Vikings WR Justin Jefferson day-to-day; no QB1 named for Week 1521 fevereiro 2025
Vikings WR Justin Jefferson day-to-day; no QB1 named for Week 1521 fevereiro 2025 -
 Vikings WR Justin Jefferson says he's playing Sunday21 fevereiro 2025
Vikings WR Justin Jefferson says he's playing Sunday21 fevereiro 2025 -
 This really reminds me of the games I play when I was a kid - Ultima Souls M(울티마 소울즈) - TapTap21 fevereiro 2025
This really reminds me of the games I play when I was a kid - Ultima Souls M(울티마 소울즈) - TapTap21 fevereiro 2025 -
 Playing as Sam Fisher in Ghost Recon Breakpoint or at least Sam Fisher's skin makes me forget i'm playing Ghost Recon. : r/Splintercell21 fevereiro 2025
Playing as Sam Fisher in Ghost Recon Breakpoint or at least Sam Fisher's skin makes me forget i'm playing Ghost Recon. : r/Splintercell21 fevereiro 2025 -
 iPhone XR Dabbing Unicorn Russia Ice Hockey Fans Jersey Winter Sports Case21 fevereiro 2025
iPhone XR Dabbing Unicorn Russia Ice Hockey Fans Jersey Winter Sports Case21 fevereiro 2025
você pode gostar
-
 Cat girls are the greatest - iFunny21 fevereiro 2025
Cat girls are the greatest - iFunny21 fevereiro 2025 -
 EU4 - Development Diary - 31st March 201621 fevereiro 2025
EU4 - Development Diary - 31st March 201621 fevereiro 2025 -
 Did Belle Delphine Get Arrested?21 fevereiro 2025
Did Belle Delphine Get Arrested?21 fevereiro 2025 -
 Friends Songs, Music album covers, Music collage21 fevereiro 2025
Friends Songs, Music album covers, Music collage21 fevereiro 2025 -
![PREORDER CLOSED] Statue [PC HOUSE] - Grass Type Pokémon – POKÉ GALERIE](http://pokegalerie.com/cdn/shop/products/IMG_6457.jpg?v=1678023179) PREORDER CLOSED] Statue [PC HOUSE] - Grass Type Pokémon – POKÉ GALERIE21 fevereiro 2025
PREORDER CLOSED] Statue [PC HOUSE] - Grass Type Pokémon – POKÉ GALERIE21 fevereiro 2025 -
 Everything You Need to Know About Using Hip Fire in COD Mobile21 fevereiro 2025
Everything You Need to Know About Using Hip Fire in COD Mobile21 fevereiro 2025 -
 Pokemon Zarude MS-40 2 Inch Figurine : Home & Kitchen21 fevereiro 2025
Pokemon Zarude MS-40 2 Inch Figurine : Home & Kitchen21 fevereiro 2025 -
 Manchester United manager Erik ten Hag told Noa Lang to 'shut up21 fevereiro 2025
Manchester United manager Erik ten Hag told Noa Lang to 'shut up21 fevereiro 2025 -
 How to Choose a Reliable Website to Buy ESO Gold21 fevereiro 2025
How to Choose a Reliable Website to Buy ESO Gold21 fevereiro 2025 -
 zombine with a shotgun — HL2 beta Alyx. i tried some loose painting this21 fevereiro 2025
zombine with a shotgun — HL2 beta Alyx. i tried some loose painting this21 fevereiro 2025